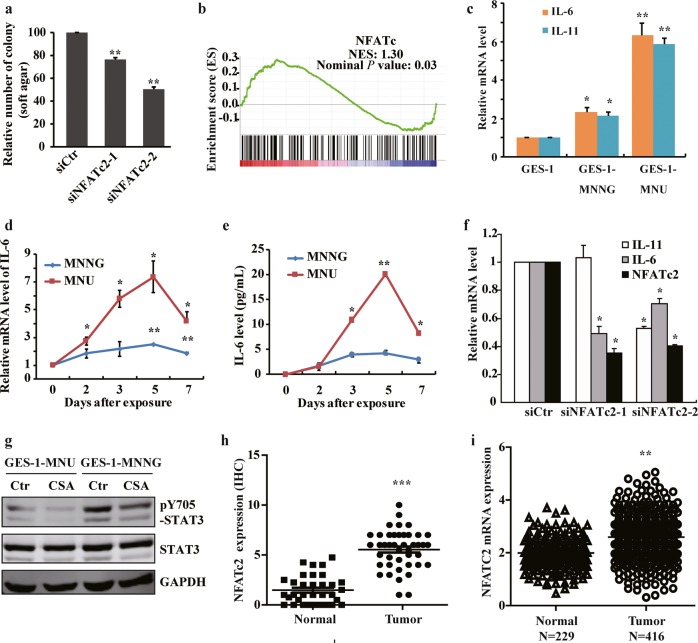
Fig. 5. NFATc2 contributes to gastric carcinogenesis by affecting the inflammatory pathways.
a Cell anchorage-independent growth in transformed cells with NFATC2 siRNA knockdown. b Gene set enrichment plots of differentially expressed genes belonging to the NFATc pathway in NOC-treated cells. P value is determined by GSEA software. c IL-6 and IL-11 mRNA expression in malignant transformed cells by RT-qPCR. d IL-6 expression by PCR after NOC treatment at different times. e IL-6 production detected by ELISA after NOC treatment at different times. f RT-qPCR analysis of IL-6 and IL-11 mRNA levels after knockdown NFATc2 by siRNA. g The transformed cells were treated by cyclosporine A (CSA) 10 μM for 24 h, and STAT3 Y705 phosphorylation was detected by WB. h and i NFATc2 expression in 52 paired gastric cancer tissues by IHC, and TCGA database analysis, respectively. The analyses were repeated three times, and the results were expressed as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.