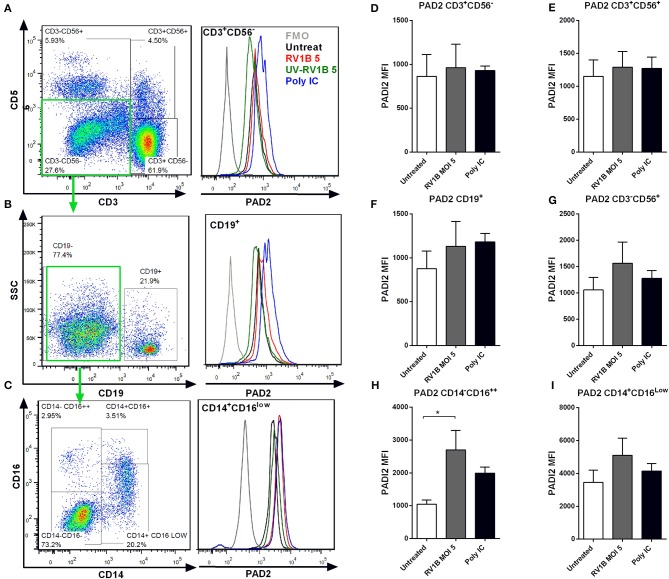
Figure 4.
Human rhinovirus and Poly I:C stimulation increase PAD2 expression in CD14−CD16++ PBMCs. Peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) were isolated and exposed to different doses of HRV (viral MOI of 1 or 5) or to 10 μg/ml of Poly I:C for 24 or 48 h. Intracellular PAD2 expression was assessed in different PBMC subsets by FACS. Dot plots indicate the gating strategy used and histogram overlays indicate representative PAD2 levels (MFI) in different PBMCs subsets, (A) CD3+ CD56− T-cells, (B) CD19+ CD3− CD56− B-cells, and (C) CD14+ CD16low CD19− CD3− CD56− Monocytes. Bars represent the Mean Fluorescence Index (MFI) of PAD2 levels expressed in each PBMC subset after 48 h of infection: (D) T-cells, (E) NK-T cells, (F) NK-cells, (G) B-cells, (H) CD14− CD16++ monocytes, and (I) CD14+ CD16low monocytes. Bars indicate the mean ± SEM of three different experiments. Statistical analysis was performed by a one way ANOVA with Tukey's multiple comparisons test (*p ≤ 0.05).