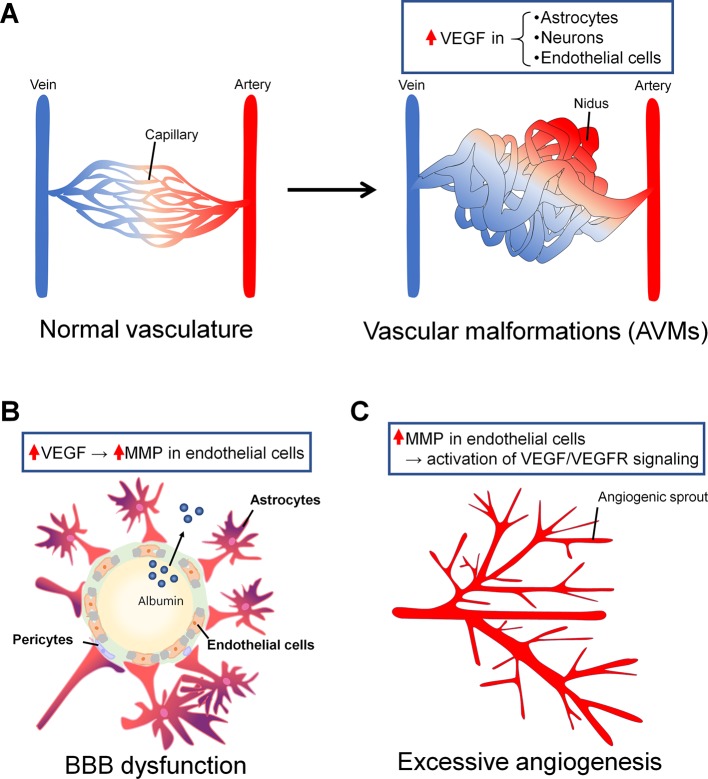
Figure 2.
Vascular abnormalities in epilepsy associated with vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). (A) Arteriovenous malformations (AVMs) are one of the major vascular malformations found in the epileptic brain. In normal vasculature, arteries and veins are connected by capillaries (right). In AVMs, there are some regions in which arteries and veins are not connected by capillaries and are instead directly connected by blood tumors called niduses (left). In astrocytes, neurons, and endothelial cells around and in niduses, VEGF expression is increased. (B) BBB dysfunction can be a cause or a consequence of epilepsy, or it can be both a cause and a consequence at the same time. BBB dysfunction induces albumin leakage and resistance to antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). VEGF induces an increase in MMP levels in endothelial cells, leading to BBB leakage. Albumin leaked from the blood flow binds AEDs and promotes drug resistance. (C) Angiogenesis is associated with BBB dysfunction in the epileptic brain. Neo vessels sprout from the pre-existing vessels. Matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) overexpression in endothelial cells could induce increases in VEGF/VEGFR signaling levels and angiogenesis.