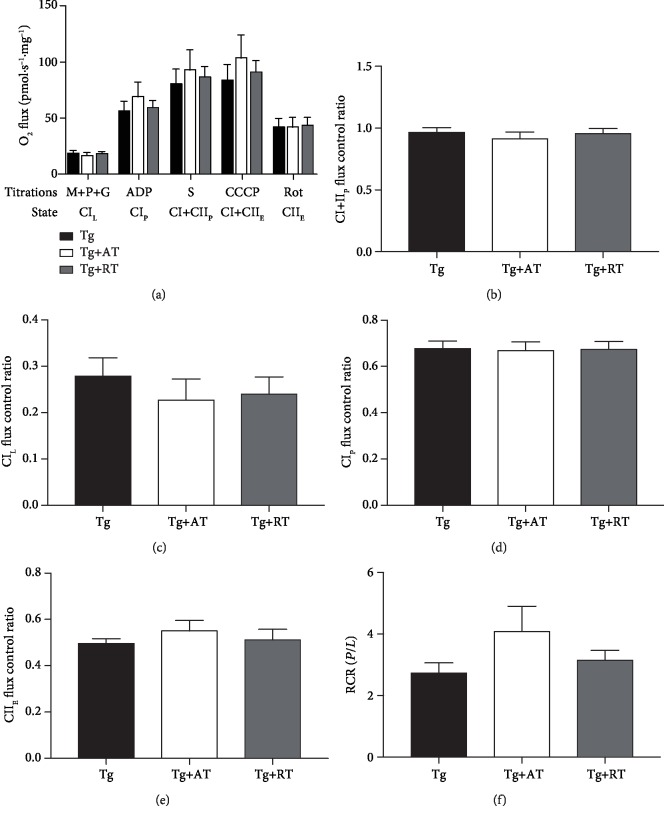
Figure 3.
Unaffected mitochondrial respiration of the hippocampus in exercise-trained 3xTg-AD mice. (a) Mass-specific oxygen (O2) flux of the hippocampus determined in situ by a substrate-uncoupler-inhibitor titration protocol, including complex I-supported LEAK (CIL) through addition of malate, pyruvate, and glutamate (M+P+G); complex I-supported oxidative phosphorylation (OXPHOS) (CIP) by addition of adenosine diphosphate (ADP); complex I+II-supported OXPHOS (CI+IIP) by addition of succinate (S); maximal electron transfer system (ETS) capacity (CI+IIE) by stepwise titration of carbonyl cyanide m-chlorophenyl hydrazine (CCCP); and complex II ETS (CIIE) by addition of rotenone (Rot). (b) Respiratory control ratio (RCR) determined by dividing CIP by CIL. (c–f) Flux control ratios were calculated by normalizing mass-specific fluxes to maximal electron transfer system capacity (CI+IIE). Shown are flux control ratios for (c) CIL, (d) CIP, (e) CI+IIP, and (f) CI+IIE. Data presented as mean ± SE. Tissues assayed from the nonexercised group (Tg), the aerobic-trained group (Tg+AT), or the resistance-trained group (Tg+RT) (n = 10/group). Differences determined by one-way ANOVA.