Figure 1.
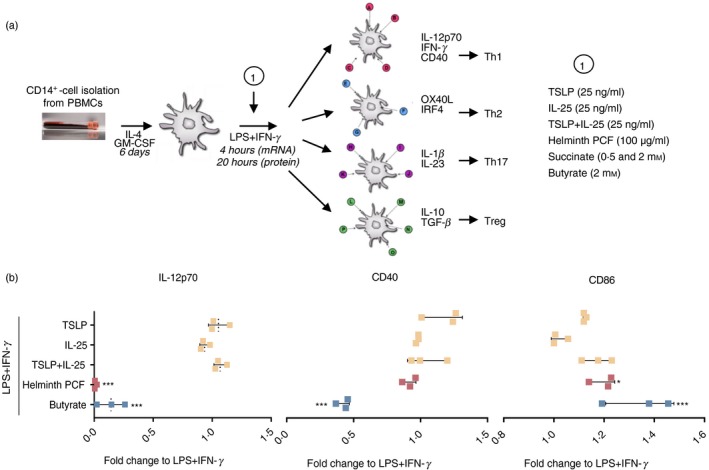
Helminth pseudocoelomic fluid (PCF) and butyrate suppress lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ)‐induced interleukin‐12p70 (IL‐12p70) secretion in monocyte‐derived dendritic cells (moDCs). (a) Overview of study design: (i) isolation of CD14+ monocytes from human blood peripheral blood mononuclear cells, (ii) differentiation of monocytes into dendritic cells (moDCs) using recombinant human IL‐4 and granulocyte–macrophage colony‐stimulating factor (GM‐CSF) for 6 days, (iii) stimulation of moDCs with indicated compounds (1), (iv) collection and preparation of samples for RNA‐seq, flow cytometry and ELISA analyses. End‐point measures are the type of transcripts (mRNA; RNA‐seq, 4 hr of stimulation), surface marker expression (flow cytometry, 20 hr) and cytokines (proteins, 20 hr) produced by the stimulated moDCs. The figure also displays the specific molecules guiding naive T helper cell polarization into different effector T cells. GM‐CSF, granulocyte–macrophage colony‐stimulating factor; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; IFN‐γ, interferon‐γ; PCF, pseudocoelomic fluid; Th1, type 1 T helper cells; Th2, type 2 T helper cells; Th17, type 17 T helper cells; Tregs, regulatory T cells. (b) Concentration of secreted IL‐12p70 in cell‐free culture supernatant and expression of the co‐stimulatory molecules CD40 and CD86 in moDCs stimulated with the indicated compounds relative to LPS + IFN‐γ only. Final concentrations of the compounds were as follows: IL‐25: 25 ng/ml, TSLP: 25 ng/ml, PCF: 100 μg dry matter/ml, Butyrate: 2 mm. Levels of IL‐12p70, CD40 and CD86 in LPS + IFN‐γ‐stimulated moDCs were: IL‐12p70: 4641·8 ± 688·1 pg/ml, CD40: 1647 ± 361 MFI, CD86: 2424 ± 311 MFI. MFI, median fluorescence intensity, mean ± SD. The experiment was performed using moDCs from three different donors. *P < 0·05, ***P < 0·001 by one‐way analysis of variance and Dunnett's post‐test for multiple comparisons to LPS + IFN‐γ.
