Figure 2.
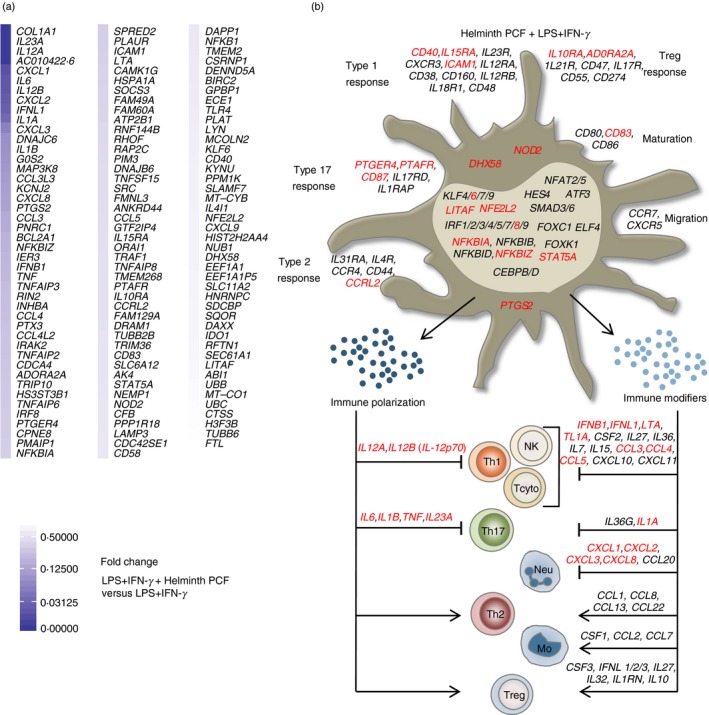
Helminth pseudocoelomic fluid (PCF) predominantly targets T helper type 1 (Th1) and Th17 polarizing abilities in pro‐inflammatory monocyte‐derived dendritic cells (moDCs). (a) Differentially expressed genes arranged by fold change in PCF + lipopolysaccharide (LPS) + interferon‐γ (IFN‐γ) ‐stimulated moDCs compared with LPS + IFN‐γ only. All genes (131) with a q‐value < 0·1 are shown. (b) Predicted phenotype of moDCs based on their transcriptional profile. The illustration focuses mainly on molecules from moDCs involved in the polarizing signals provided to naive T helper cells. Shown are the differentially regulated genes with a q‐value < 0·1. Black: genes up‐regulated by LPS + IFN‐γ (relative to unstimulated moDCs), Red: genes down‐regulated by PCF + LPS + IFN‐γ (relative to LPS + IFN‐γ only). Th1, type 1 T helper cells; NK, natural killer cells; Tcyto, cytotoxic T cells; Th17, type 17 T helper cells; Neu, neutrophils; Th2, type 2 T helper cells; Mo, monocytes; Tregs, regulatory T cells.
