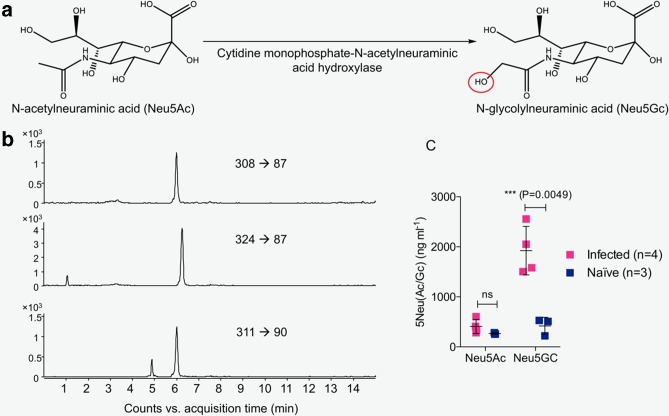
Fig. 3.
Analysis of free Sia in mouse serum using LC-MRM-MS. (a) Chemical structures of Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc. Neu5Ac is converted to Neu5Gc by the enzyme cytidine monophosphate-N-acetylneuraminic acid hydroxylase, which is only found in non-human mammals. The red circle indicates the difference between Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc. (b) LC-MRM-MS-extracted ion chromatograms of N-acetylneuraminic acid (top panel) and N-glycolylneuraminic acid (middle panel) in serum from DENV-infected mice and [13C3]-N-acetylneuraminic acid spiked into the serum (bottom panel) are shown. Three ion transitions of each compound were monitored for MRM detection; here quantifier ion transitions are shown. (c) LC-MRM-MS was used to quantify Neu5Ac and Neu5Gc in serum from mice infected with ADE 3×105 p.f.u. DENV2 D220 or uninfected (naïve) mice. Free sialic acid in the form of Neu5Gc, the predominant species in mouse serum, was increased in samples from mice with severe dengue disease. Mean±sd; P-values as indicated (two-sided Student t-test). Data were pooled from a minimum of two similar experiments. ns, not significant.