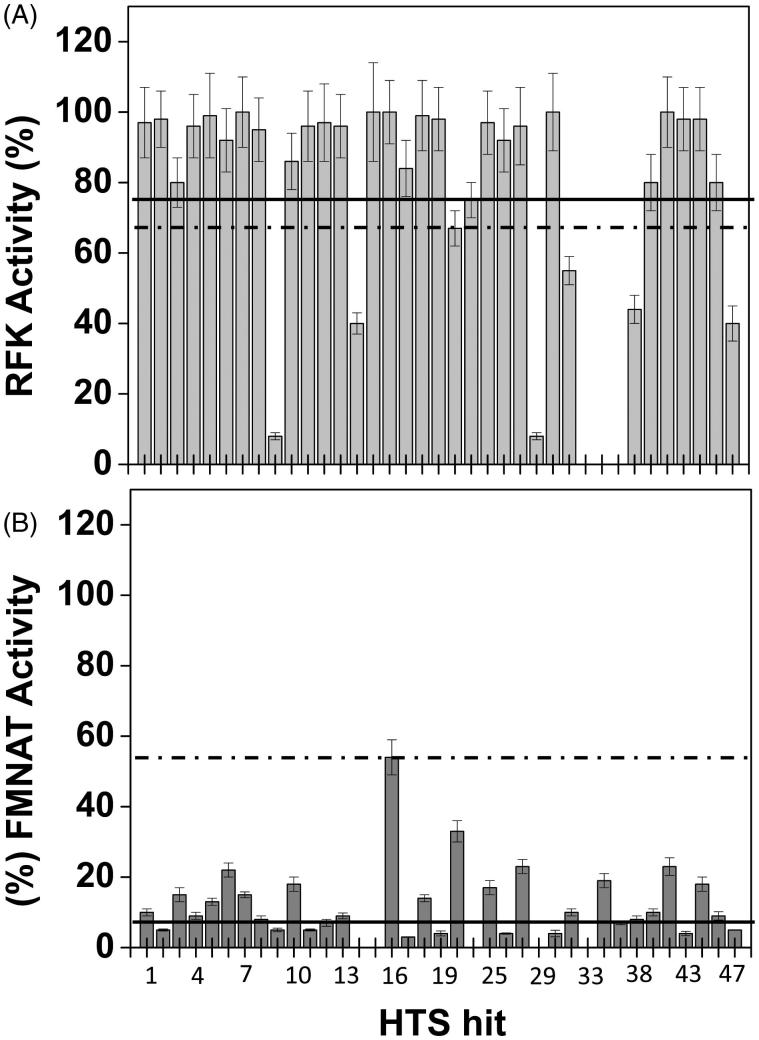
Figure 2.
Effect of the HTS hits on the RFK and FMNAT activities of CaFADS. Residual (A) RFK and (B) FMNAT activities when assayed in the presence of 250 μM of the 37 HTS hits. In (A), the columns below the dashed line present statistical significant inhibition by the corresponding hit (p < 0.002, 67% remaining activity) related to the control CaFADS RFK activity. In (B), all hits produce statistical significant inhibition (p < 0.0001, dashed line) when compared with the controls of the CaFADS FMNAT activity. Solid lines indicate 75 and 5% of the control RFK and FMNAT activities, respectively. The HTS hits displaying <5% and >75% of the control FMNAT and RFK activities, respectively, were selected for further study. Experiments carried out in 20 mM PIPES, pH 7.0, 2.5% DMSO at 25 °C, with 7.5 μM RF, 350 μM ATP, 0.8 mM MgCl2 (for the RFK activity) or 15 μM FMN, 350 μM ATP, 10 mM MgCl2 (for the FMNAT activity) (n = 3; mean ± SD).