Figure 4.
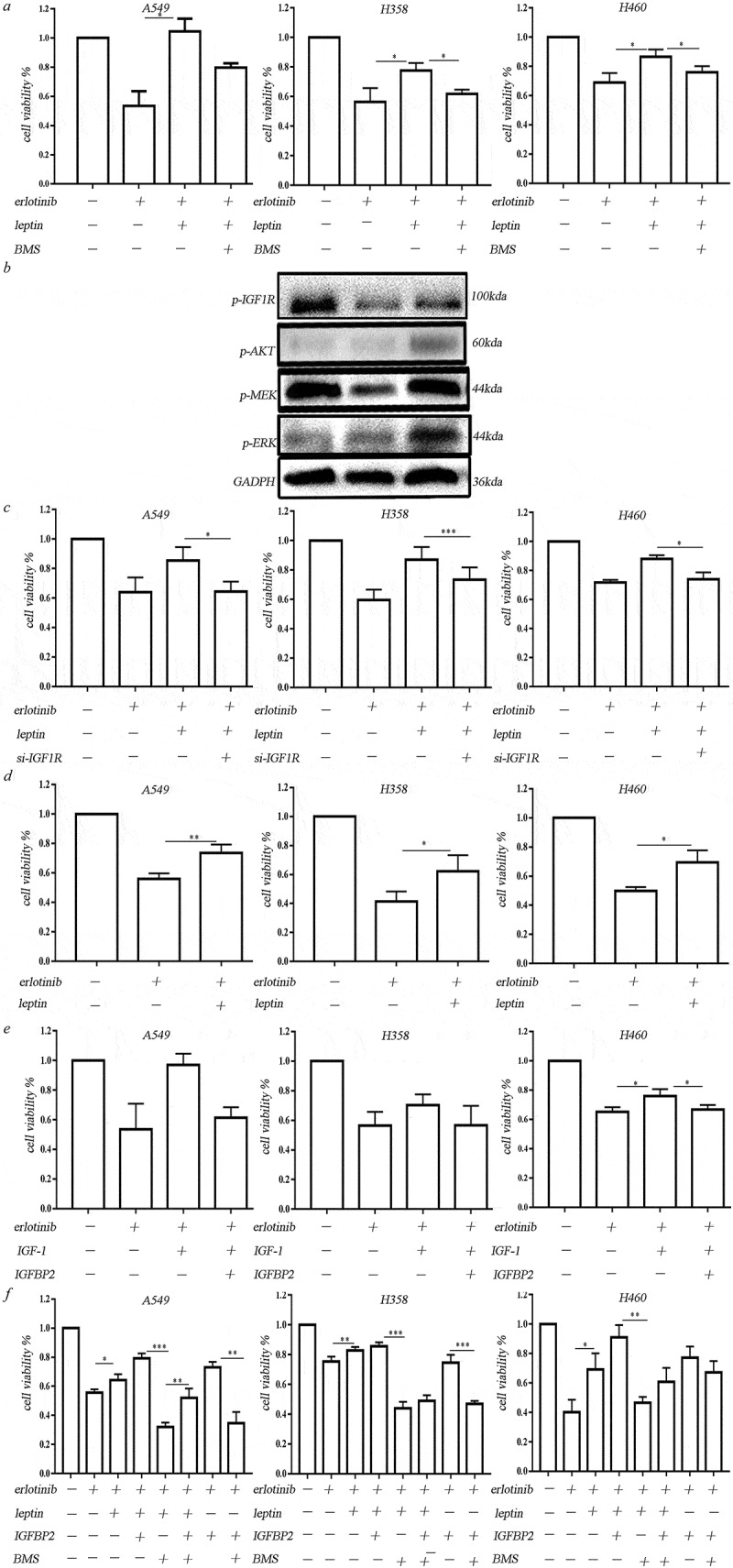
Leptin increased erlotinib resistance in lung cancer cells by activating IGF-1R signaling in hypoxia. (a) IGF-1R inhibitor BMS-754807 could significantly reverse the erlotinib resistance mediated by leptin. (b) Western blot analysis of IGF-1R phosphorylation and downstream MEK/ERK and AKT signaling induced by leptin. (c) Transfection of IGF-1R-siRNA in lung cancer cells before treatment of leptin resulted in the sensitization of lung cancer cells to erlotinib. (d) Leptin increased the growth of erlotinib-treated lung cancer cells in the absence of IGF-1. (e) IGFBP2 could counteract the effect of IGF-1 on the erlotinib resistance. (f) IGFBP2 promoted the lung cancer cell growth after treatment of erlotinib in IGF-1 independent through activating IGF-1R signaling. CCK-8 cell viability assay was performed to evaluate cell viability after treatment of erlotinib. Results are presented as the median of three independent experiments (*p < .05, **p < .01, Student’s t test).
