Figure 1.
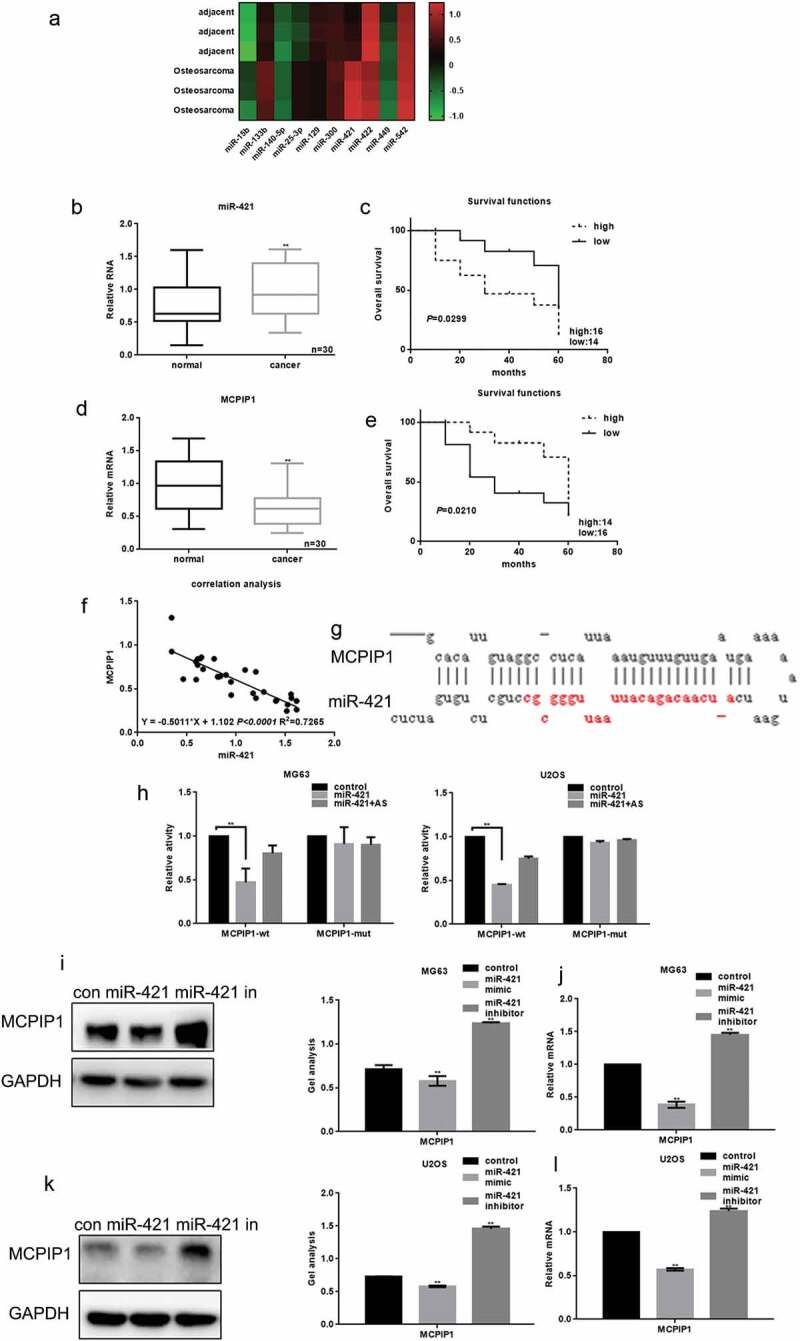
The relationship between miR-421 and MCPIP1 in osteosarcoma (a) The expressions of miR-421 and other microRNAs in 30 samples of osteosarcoma tissues and adjacent tissues were detected by real-time PCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ** P < .05 vs. adjacent tissues group (b) MiR-421 expression was markedly elevated in osteosarcoma tissues (c)The relationship between the expression of miR-421 and the survival time of osteosarcoma patients. (d) The levels of MCPIP1 in 30 samples of osteosarcoma tissues and adjacent tissues were detected by real-time PCR. The levels of MCPIP1 were strikingly decreased in osteosarcoma tissues. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ** P < .05 vs. adjacent tissues group (e) The relationship between the expression of MCPIP1 and the survival time of osteosarcoma patients. (f) The correlation between the expression of miR-421 and MCPIP1 (g) miRDB predicted that miR-421 could target MCPIP1 (h) The interaction between miR-421 and the MCPIP1 was tested by luciferase reporter assays in MG63 and U2OS cells. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ** P < .05 vs. TK-MCPIP1 group (i-l) After transfecting miR-421 mimic/inhibitor in MG63 and U2OS cells, the levels of MCPIP1 were detected by western blot and real-time PCR. Data are shown as mean ± SEM. ** P < .05.
