Fig. 1.
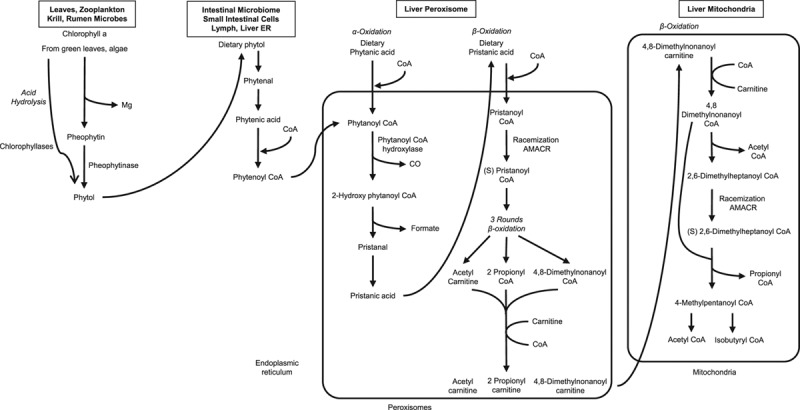
Metabolism of phytol, phytanic acid and pristanic acid. Phytol is derived from plant and phytoplankton chlorophyll. Rumen microbiota, marine zooplankton and human intestinal bacteria are able to cleave the chlorophyll porphyrin ring and release phytol. After intestinal absorption, dietary phytol is metabolized in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) via phytenal and phytenic acid to phytanoyl CoA. Dietary PA and PRA are activated on the cytosolic side of the peroxisomes to phytanoyl CoA and pristanoyl CoA. In the peroxisomes, phytanoyl CoA is α-oxidized to PRA, the racemic mixture of PRA is converted by α-methylacyl-CoA racemase (AMACR) to (2S) PRA. After three rounds of β-oxidation, 4,8-dimethylnonanoyl CoA is shuttled by carnitine into the mitochondria for complete β-oxidation, which include four rounds of β-oxidation and one racemization step using AMACR (Verhoeven and Jakobs, 2001). PA, phytanic acid; PRA, pristanic acid.
