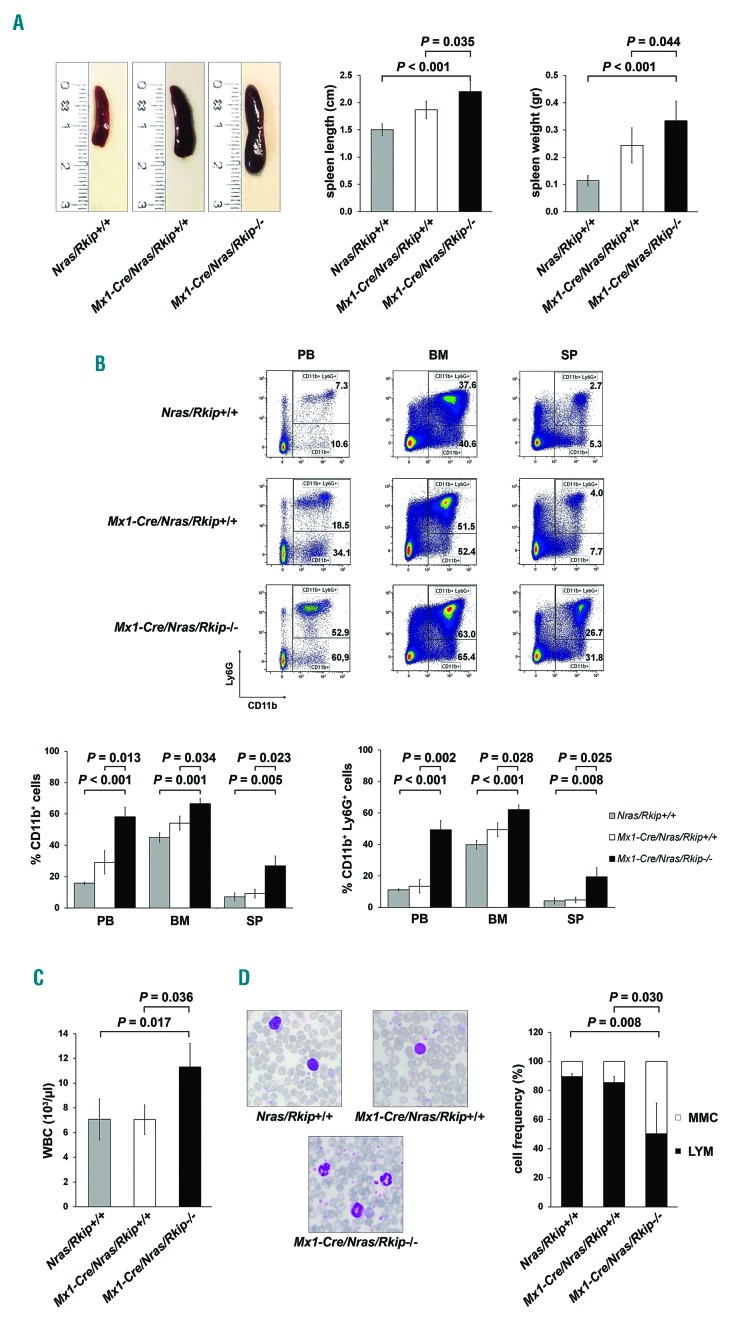
Figure 4.
Deletion of Rkip aggravates myeloproliferation and myeloproliferative disease (MPD) development in Nras-mutated mice. An Nras driven mouse model of myeloproliferation (Mx1-Cre/Nras) was used to study the effects of Rkip-/- on Ras-driven myeloproliferation and MPD development. Mice were electively killed at an age of six months after the first pIpC injection, Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip−/− mice (n=3) were compared to control mice (Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+; n=3) as well as to mice without Mx1-Cre (Nras/Rkip+/+; n=4). (A) Representative images of spleens from Nras/Rkip+/+, Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+ and Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip−/− mice as well as bar graphs of spleen lengths and weights, showing splenomegaly in animals with Rkip deletion. (B) Representative flow cytometric plots showing an increase in the percentage of CD11b+ and CD11b+ Ly6G+ myelomonocytic cells in peripheral blood (PB), bone marrow (BM) and spleen (SP) of Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip−/−mice when these were compared to Nras/Rkip+/+ animals as well as when compared to Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+ littermates. (C) Peripheral blood counts demonstrate an increased number of white blood cells (WBC) in Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip−/− mice. (D) The leukocytosis in Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip−/−mice is caused by an increased number of myelomonocytic cells (MMC), as shown in the representative PB smear and as shown in the flow cyto-metric analyses shown above. Graphs show the average ± Standard Deviation. Statistical significance was calculated by Student’s t-test. RKIP: RAF kinase inhibitor protein.