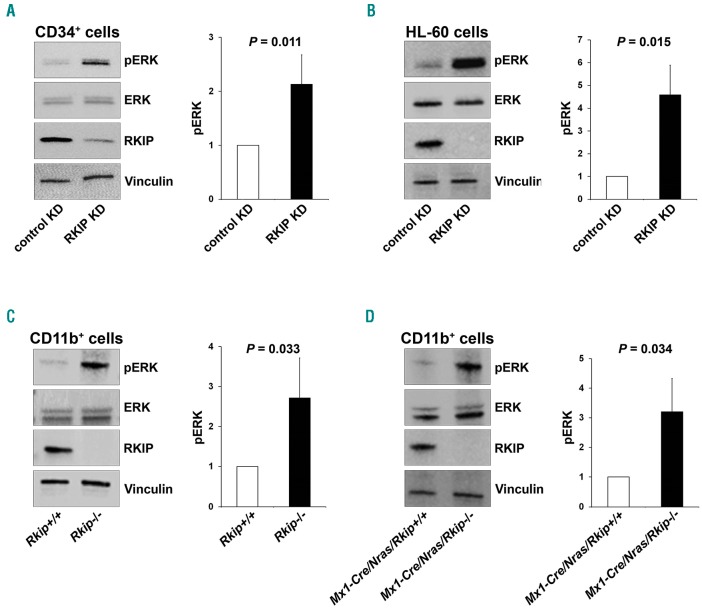
Figure 6.
RAF kinase inhibitor protein (RKIP) regulates RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling in the myeloid system. (A) RKIP shRNA knockdown (KD) in CD34+ human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPC) increased RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling, as measured by the phosphorylation of ERK (pERK). (Left) A representative immunoblot. Graph represents the mean of three independent experiments ±Standard Deviation (SD); pERK intensity is given as x-fold change to the CD34+ control KD. (B) RKIP shRNA KD in HL-60 increased pERK levels as well. (Left) Representative immunoblot. Graph represents the mean of three independent experiments ±SD; pERK intensity is given as x-fold change to the HL-60 control KD. (C) Rkip deletion enhanced the activity of RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling in CD11b+ cells isolated from the bone marrow of mice. (Left) A representative immunoblot. Graph represents the mean of three independent experiments ±SD; pERK intensity is given as x-fold change to the Rkip+/+ control genotype. (D) Rkip deletion also increased the activity of RAS-MAPK/ERK signaling in CD11b+ cells isolated from Nras-mutated mice. A representative immunoblot and the graph is presented as described above, Mx1-Cre/Nras/Rkip+/+ were used as control group. Mice experiments were performed using n=3 mice for each genotype. Statistical significance was evaluated by Student’s t-test in all cases.