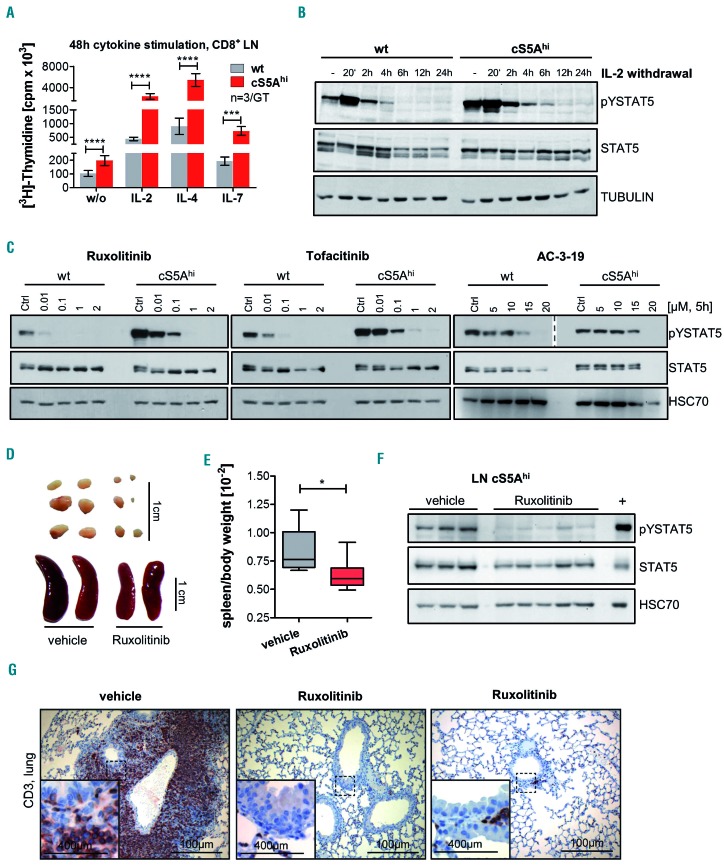
Figure 7.
Dependence of cS5Ahi on upstream cytokine signaling can be used for targeted pharmacological therapy. (A) [3H]Thymidine incorporation in CD8+ T cells isolated from lymph nodes (LN) of 35-week old wildtype (wt) and cS5Ahi mice after stimulation with interleukin (IL)-2 (100 U/mL, P≤0.0001), IL-4 (100 ng/mL, P≤0.0001), IL-7 (10 ng/mL, P=0.0002) or without (w/o) cytokines (P≤0.0001, n=3/genotype in triplicate, all unpaired t-test). (B) Immunoblot for pYSTAT5 and STAT5 on IL-2-cultured wt and cS5Ahi LN cells sampled at specific time points after IL-2 withdrawal. α-TUBULIN was used as a loading control. Representative blot of three experiments. (C) In vitro treatment of wt and cS5Ahi LN-derived T cells with increasing concentrations of ruxolitinib (left), tofacitinib (middle) or AC-3-19 (right) for 5 h blotted for pYSTAT5 (AC-3-19 – two different exposures are shown indicated by the dashed line) and STAT5. An equal amount of dimethylsulfoxide was used as a control. HSC70 served as a loading control. Representative blot of three experiments. (D) In vivo treatment of cS5Ahi mice with 45 mg/kg ruxolitinib (n=6) or vehicle (n=6) for 30 days. Macroscopic appearance of LN (top) and spleen (bottom) and (E) spleen/body weight ratio after 30 days of treatment (Mann Whitney test, P=0.026). (F) Immunoblot (representative blot of two) on LN lysates of vehicle- or ruxolitinib-treated cS5Ahi mice for pYSTAT5 and STAT5, HSC70 was used as a loading control and diseased cS5Ahi spleen lysate was used as a positive control. (G) CD3 staining of lung sections of vehicle- and ruxolitinib-treated cS5Ahi mice, scale bars represent 400 or 100 mm.