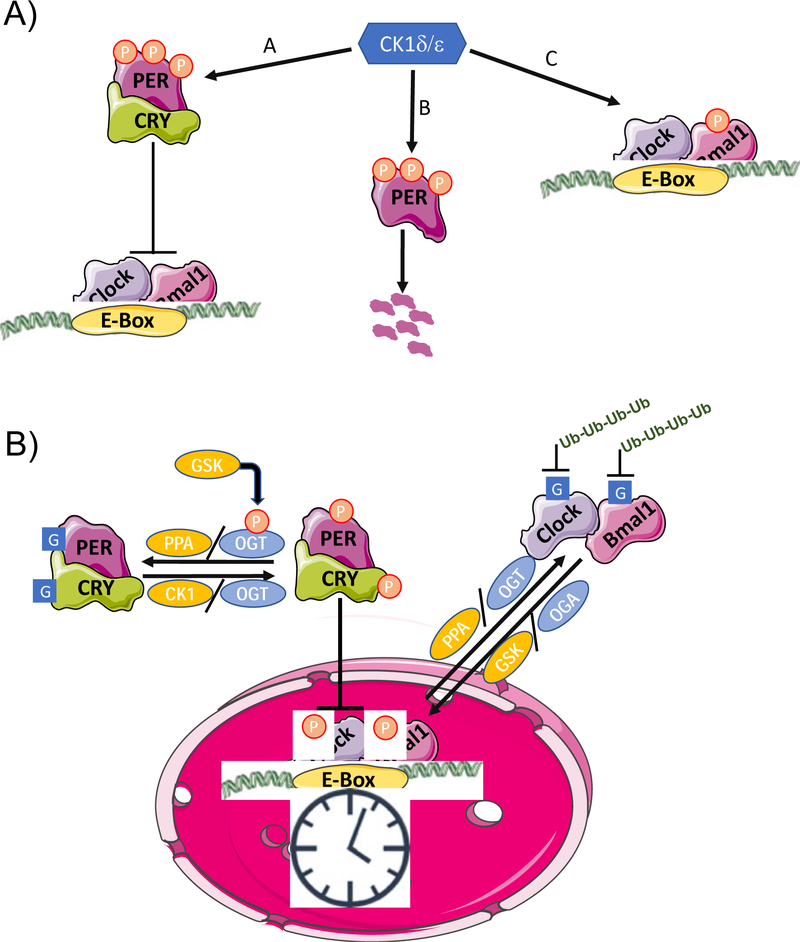
Figure 1.
A) Functions of Caesin Kinase (CK) 1d/e in the mammalian clock. A) Interaction with CRY stabilizes PER, allowing it be phosphorylated by leading to its nuclear translocation and repression of Clock/Bmal1 transcription; B) CK1δ/ε phosphorylation of PER in the cytosol leads to proteasomal degradation; C) CK1 δ/ε phosphorylation of Bmal1 increases its transcriptional activity. B) Cross-talk between phosphorylation (P) and O-GlcNAcylation (G) in the regulation of the circadian clock. GSK3β phosphorylation of OGT results in its activation, leading to O-GlcNAcylation of PER and CRY, which prevents their phosphorylation thereby repressing their effects on CLOCK/BMAL1 transcription. O-GlcNAcylation of CLOCK also represses the effects of PER. Phosphorylation and O-GlcNAcylation also play a role in regulating the ubiquitination and subsequent degradation of CLOCK and BMAL1