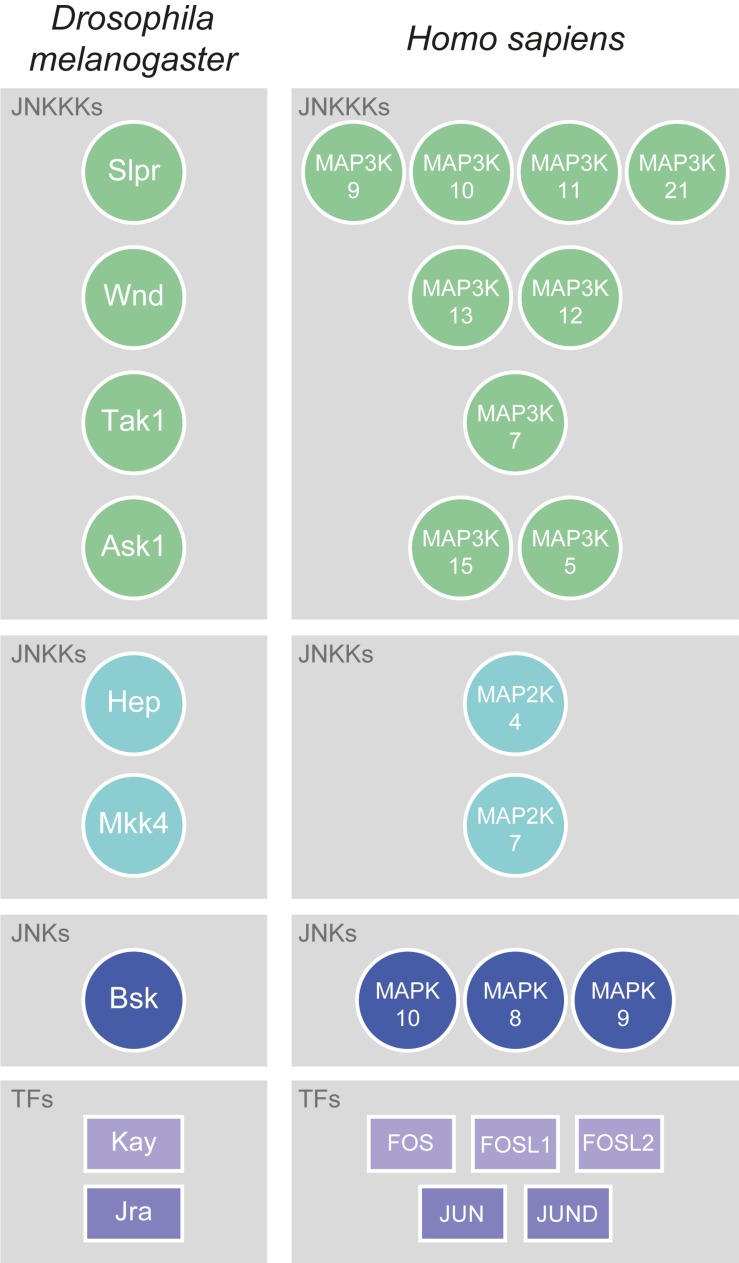
FIGURE 1.
Conservation of JNK signalling core. The kinase core of JNK signalling is well-conserved between flies and mammals. In Drosophila, there are at least four JNKKKs: Slpr (Slipper), Wnd (Wallenda), Tak1 (TGFβ-associated kinase 1), and Ask1 (Apoptotic signal-regulating kinase 1). All have multiple human orthologues, which are Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinases (MAP3Ks), with the most highly conserved being shown here. Slpr is most closely related to MAP3K9, MAP3K10, MAP3K11, and MAP3K21, Wnd to MAP3K13 and MAP3K12, Tak1 to MAP3K7, and Ask1 to MAP3K15 and MAP3K5. The Drosophila JNKKs are Hep (Hemipterous) and Mkk4 (MAP kinase kinase 4), which have human orthologues amongst the Mitogen-activated protein kinase kinases (MAP2Ks). Hep is most closely related to MAP2K4, and Mkk4 to MAP2K7. While Drosophila has only one JNK, Basket (Bsk), there are three conserved Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) orthologues to Bsk in humans: MAPK10, MAPK8, and MAPK9. JNKs upregulate the activity of various TFs, the best known of which are those that form the heterodimeric AP-1 complex. In Drosophila, those TFs are Kay (Kayak) and Jra (Jun-related antigen). In humans, the orthologues of Kay are FOS (Fos proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit), FOSL1 (FOS like 1, AP-1 transcription factor subunit), and FOSL2 (FOS like 2, AP-1 transcription factor subunit), while the orthologues of Jra are JUN (Jun proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit) and JUND (JunD proto-oncogene, AP-1 transcription factor subunit).