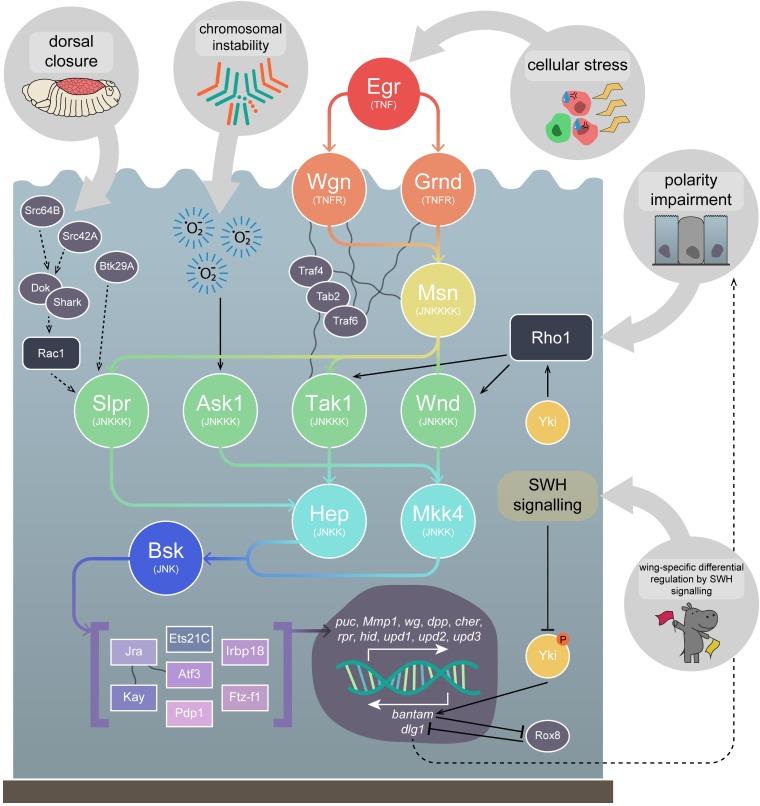
FIGURE 5.
Upstream regulation of JNK signalling. JNK signalling can be activated by a variety of different upstream mechanisms. JNK signalling mediates cell morphology changes, such as those during embryonic dorsal closure, where it is thought to act via Src42A and Src64B (and/or Btk29A) to activate the kinase Shark and its adapter, Dok. This signalling may in turn activate Rac1 and promote JNK signalling via Slpr. In cells with chromosomal instability, accumulated ROS promote Ask1 signalling, stimulating the JNK signalling pathway to promote apoptosis. Arguably, the best understood pathway is the TNF-JNK signalling pathway, which is generally considered to be activated as a response to cellular stresses. Egr, the Drosophila TNF, binds to Grnd or Wgn (TNFRs), which activate Msn (JNKKKK) and Tak1 (JNKKK), via the adapter proteins Traf4, Tab2, and Traf6. JNK signalling is activated in polarity-impaired cells, which is thought to occur via the stimulation of Wnd by the actin cytoskeleton regulator Rho1, although TNF signalling contributes to amplify JNK activity. Lastly, in Drosophila wing imaginal discs, differential JNK signalling regulation by the SWH signalling pathway has been observed. While non-active SWH signalling allows Yki to promote JNK activation via Rho1, activated SWH signalling suppresses Yki activity, preventing bantam transcription, a miRNA that suppresses Rox8, which acts as a positive regulator of JNK signalling, possibly by downregulating dlg1. Msn is thought to be capable of activating Tak1, Wnd, and Slpr, but has not yet been shown to activate Ask1. Tak1, Wnd, and Ask1 are then thought to be capable of activating both the JNKKs, Hep and Mkk4, while Slpr has only yet been shown to act via Hep. Both Hep and Mkk4 can activate the sole Drosophila JNK, Bsk, which positively regulates a number of TFs, including the well known Jra and Kay. These TFs promote transcription of a number of important genes, including the apoptosis promoters hid and rpr, the Jak-STAT ligands upd1, upd2, and upd3, the invasion promoter Mmp1, and the negative JNK regulator puc. Dotted lines represent uncertain interactions. Wavy lines represent known physical interactions between core pathway members and (their adapters. Gene and protein name abbreviations used in the diagram are as follows: Src oncogene at 64B (Src64B), Src oncogene at 42A (Src42A), Btk family kinase at 29A (Btk29A), Downstream of kinase (Dok), SH2 ankyrin repeat kinase (Shark), Eiger (Egr), Grindelwald (Grnd), Wengen (Wgn), Misshapen (Msn), TNF-receptor-associated factor 4 (Traf4), TAK1-associated binding protein 2 (Tab2), TNF-receptor-associated factor 6 (Traf6), Slipper (Slpr), Wallenda (Wnd), TGF-β activated kinase 1 (Tak1), Apoptotic signal-regulating kinase 1 (Ask1), Hemipterous (Hep), MAP kinase kinase 4 (Mkk4), Basket (Bsk), Jun-related antigen (Jra), Kayak (Kay), Ets at 21C (Ets21C), Activating transcription factor 3 (Atf3), PAR-domain protein 1 (Pdp1), Inverted repeat binding protein 18 kDa (Irbp18), Ftz transcription factor 1 (Ftz-f1), puckered (puc), Matrix metalloproteinase 1 (Mmp1), wingless (wg), decapentaplegic (dpp), cheerio (cher), reaper (rpr), head involution defective (hid), unpaired 1 (upd1), unpaired 2 (upd2), unpaired 3 (upd3), Yorkie (Yki), discs large 1 (dlg1).)