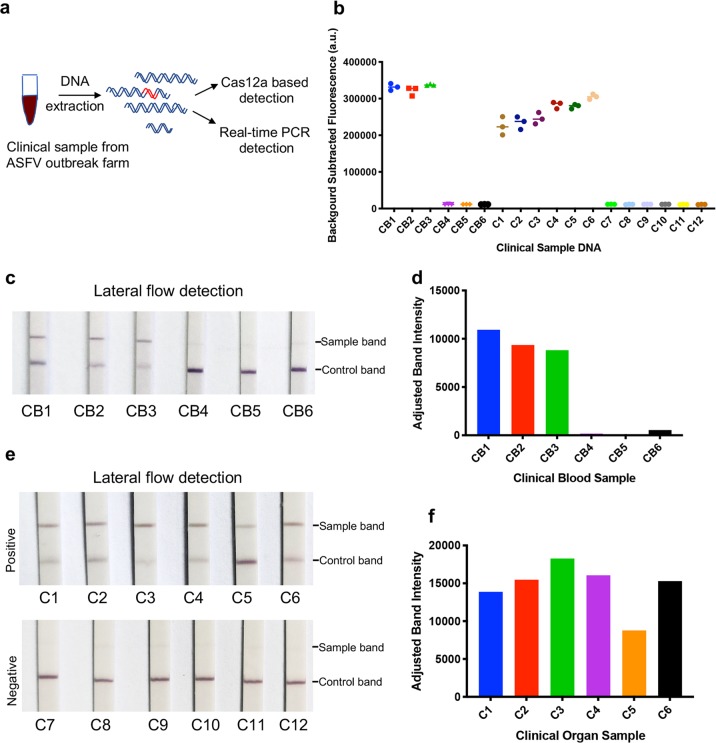
Fig. 3. ASFV detection in clinical samples with CRISPR/Cas12a lateral flow detection.
a Schematic of ASFV detection from the clinical samples with both CRISPR/Cas12a-LFD and real-time PCR. Six blood samples (CB1 to CB6) and twelve organ samples collected from a pig farm that experienced an ASFV outbreak. The DNA was extracted and detected with both real-time PCR and CRISPR/Cas12a-LFD. b ASFV detection in clinical samples using CRISPR/Cas12a coupled with fluorescence readout. The fluorescence value of the negative sample was set as the background fluorescence. The detection fluorescence values were calculated by subtracting the background fluorescence value from the value of the sample detection. Samples CB1 to CB3 and C1 to C6 were positive. c ASFV detection in blood samples with CRISPR/Cas12a-LFD. The DNA of clinical blood samples was added to the CRISPR/Cas12a reaction system with ASFV-specific crRNAmix. After a 30 min incubation at 37 °C, the CRISPR/Cas12a reaction sample was detected with lateral flow strips at room temperature for 3 min. CB1 to CB3 were positive, which was consistent with CRISPR/Cas12a-FD and real-time PCR detection. d Quantitation of sample bands at the test line in (c). The sample bands were scanned and analysed with ImageJ software. e ASFV detection in organs with CRISPR/Cas12a-LFD. The detection procedure was the same as the blood DNA detection. C1 to C6 were ASFV positive, and C7 to C12 were ASFV negative. f Quantitation of sample bands at the test line in (e). The sample bands were scanned and analysed with ImageJ software.