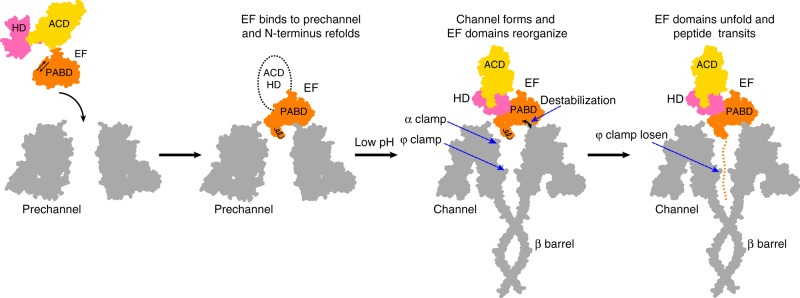
Fig. 4. Mechanism of EF translocation.
Illustration of the anthrax toxin channel translocation steps with EF. Initially, EF binds to the PA pre-channel, and the N-terminal α helix of the PABD of EF docks into the α clamp, yielding the space for domain reorganization of EF. After the PA pre-channel changes to the channel state at low pH, the destabilization of the interface between the PABD of EF and the PA channel allows the N-terminal α helix to translocate down to the ϕ-clamp site. In parallel, the α clamp engages the EF polypeptide again, causing an allosteric change in the ϕ clamp. The change in the ϕ clamp applies force to the α helix, changing its conformation to extended chain and driving it past the charge clamp site located near the top of the β barrel. The cycle repeats on the next section of EF polypeptide.