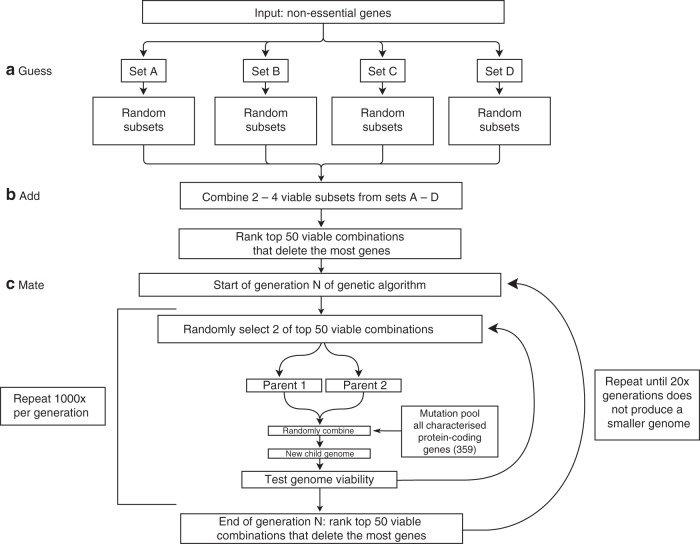
Fig. 2. GAMA algorithm for genome design.
a Only non-essential genes whose knockout does not prevent cell division are deletion candidates and are equally divided into Sets A–D. Four hundred random deletion subsets are produced and simulated per set, each containing 50–100% of the genes within the set. Deletion subsets that do not prevent division (“viable”) go to the next stage. b 3000 combinations of deletion subsets are generated and simulated. c This is a cyclical step. The mutation pool targets a random number of genes for alteration (both knock-ins and knockouts), including essential genes. Simulation data generated by the GAMA algorithm is available37 (see Data availability section). Details of simulations settings are available in the Methods section.