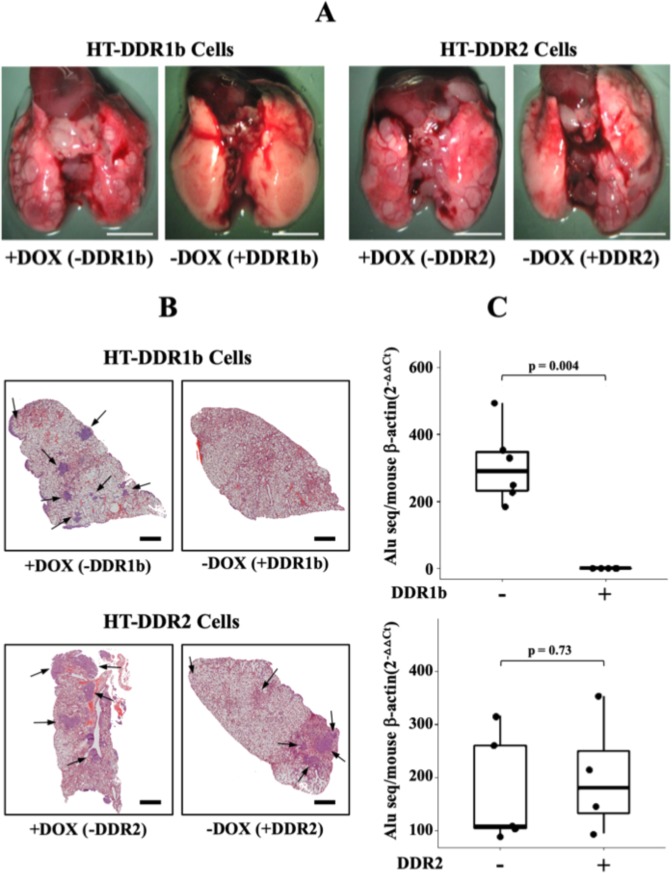
Figure 5.
DDRs differentially regulate the lung colonizing ability of intravenously inoculated HT1080 cells. HT-DDR1b and HT-DDR2 cells were incubated for two days with or without DOX to repress or induce DDRs, respectively. Then, the cells were harvested, and 1 × 106 cells/mouse were inoculated into the tail vein of mice that were fed a regular or a DOX-supplemented diet. After ~20 days, mice were euthanized, and the lungs were harvested and examined for macroscopic (A) and microscopic (B) tumour colonies, and for human DNA Alu sequences (C). (A) Gross anatomical photos of lungs of mice inoculated with either HT-DDR1b or HT-DDR2 cells ±DOX treatment. (B) H&E sections of lungs from mice inoculated with HT-DDR1b or HT-DDR2 cells ±DOX treatment. Arrows indicate tumour cell colonies. (C) Human Alu qPCR analyses of lungs (right three lobes) of mice inoculated with either HT-DDR1b or HT-DDR2 cells. −DDR1b (n = 6), +DDR1b (n = 5), −DDR2 (n = 5), and +DDR2 (n = 4). Statistical analyses were performed using Mann-Whitney U test, as described in the Methods section.