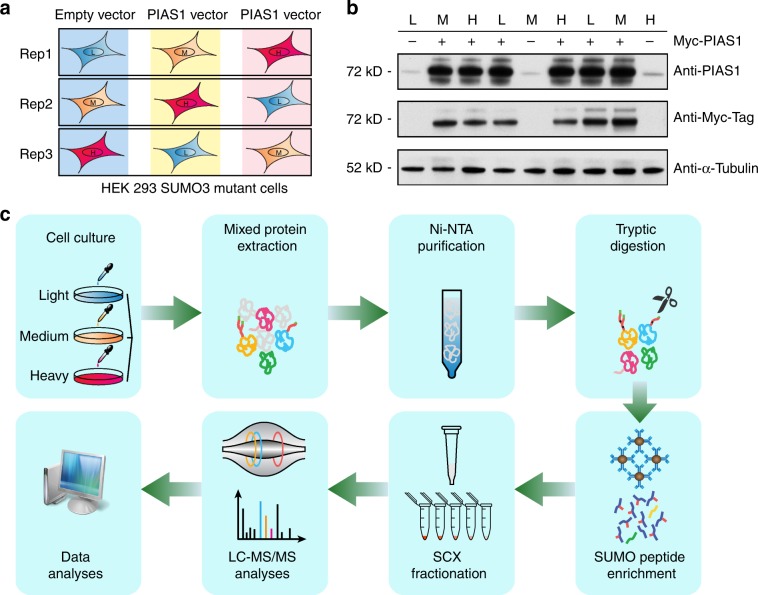
Fig. 2. Workflow for the identification of PIAS1 substrates.
a HEK293-SUMO3m cells were cultured in SILAC medium with reverse labeling in biological triplicates. For replicate 1, PIAS1 overexpression was performed in medium and heavy channels with Myc-PIAS1 vector, whereas the cells cultured in light media were transfected with the pcDNA3.0-Myc vector (empty vector). For replicates 2 and 3, the empty vector was transduced in the medium and heavy labeled cells, respectively. b Western blotting showing the level of overexpression of PIAS1 in the transfected cells. Detection of PIAS1 overexpression by both Anti-PIAS1 antibody and Anti-Myc antibody. α-Tubulin was used as loading control. c SILAC-labeled cells were lysed and combined in a 1:1:1 ratio based on protein content. SUMOylated proteins were enriched from the cell extract on an IMAC column prior to their tryptic digestion. After desalting and drying, peptides containing the SUMO3 remnant were enriched using a custom anti-K-ε-NQTGG antibody that was crosslinked on magnetic beads. Enriched peptides were further fractionated on SCX columns and injected on a Tribrid Fusion mass spectrometer. Peptide identification and quantification were performed using MaxQuant. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.