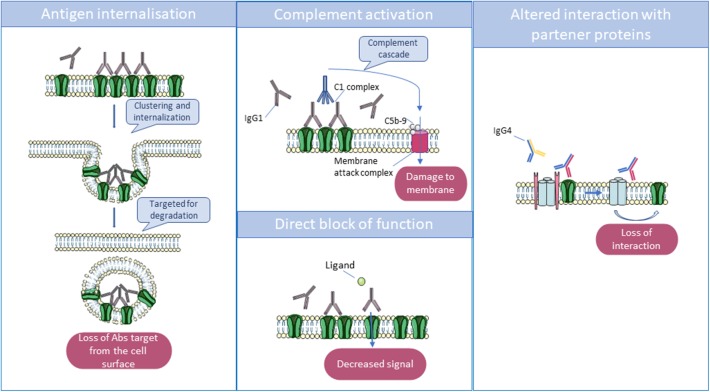
Figure 2.
Main mechanisms by which antibodies act to reduce the function of their targets. Immunoglobulin G1 (IgG1) and IgG3 can cross-link antigenic targets, leading to internalization, and degradation of the antigen in lysosomes. Also, IgG1 and IgG3 can activate the complement cascade via their Fc domains, which interact with complement proteins C1 and C1q. The complement cascade culminates in the formation of the membrane attack complex which disrupts the phospholipid bilayer, resulting in cell damage. Finally, some autoantibodies can directly block receptors by binding to an essential transmitter or regulatory binding site, but monovalent IgG4 can only act by disrupting the function of the target or the interaction between their target and partner proteins.