Figure 7.
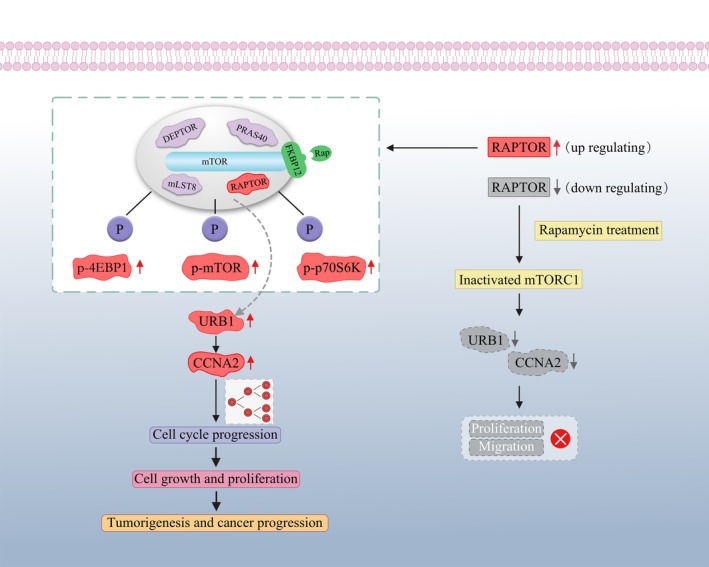
Schematic diagram showing the effect of regulatory associated protein with mammalian/mechanistic target of rapamycin (RAPTOR) on tumorigenesis and progression of colorectal cancer (CRC) by targeting URB1. Upregulation of RAPTOR promotes proliferation and cell cycle progression of CRC cells by inducing mTORC1 signaling and upregulating URB1 and cyclinA2 (CCNA2) expression. RAPTOR silencing or rapamycin treatment inactivates mTOR complex 1 and impairs URB1 and CCNA2 transcription, which blocks the proliferation and cell cycle transition and induces apoptosis of CRC cells
