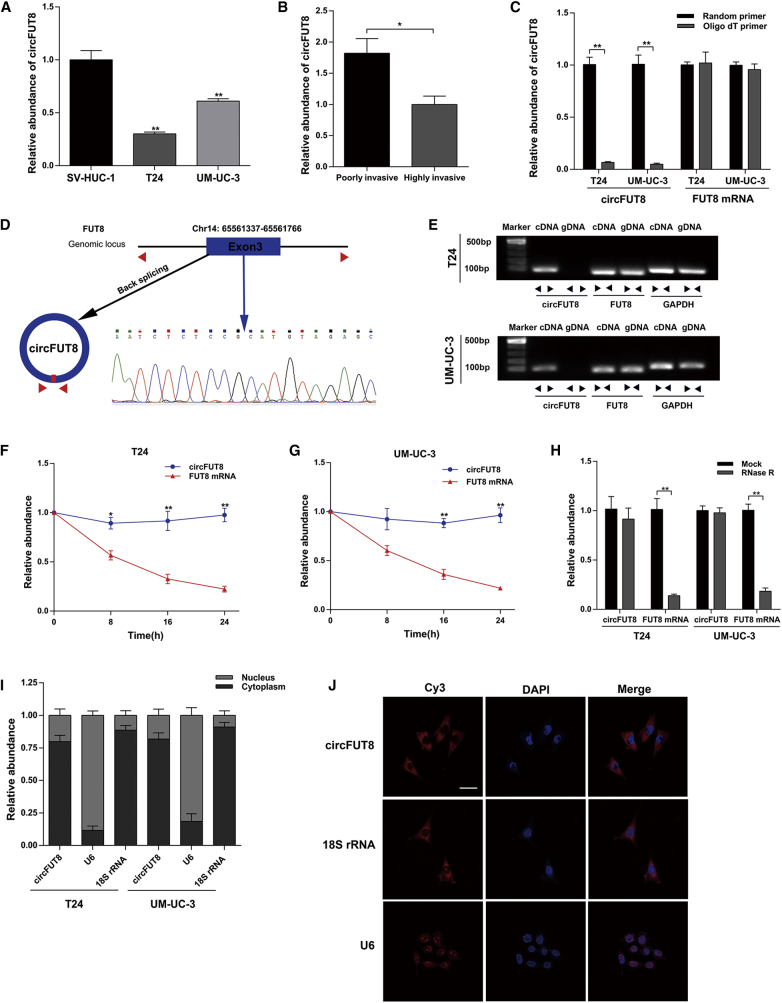
Figure 1.
The Identification and Abundance of circFUT8 in BCa and the Subcellular Location of circFUT8
(A) The relative abundance of circFUT8 in SV-HUC-1, T24, and UM-UC-3 was detected by quantitative real-time PCR. (B) The relative abundance of circFUT8 in our established poorly and highly invasive T24 cell sublines. (C) The abundance of circFUT8 and FUT8 mRNA was detected by quantitative real-time PCR with reverse transcription products using random primer or oligo(dT) primer. (D) Schematic diagram demonstrating that exon 3 derived from FUT8 formed the circFUT8. The back-splicing junction site of circFUT8 was validated by Sanger sequencing. The blue arrow indicates the special back-splicing junction of circFUT8. (E) The existence of circFUT8 was validated in the T24 and UM-UC-3 cell lines by gel electrophoresis using the products of quantitative real-time PCR. (F and G) The relative abundance of circFUT8 and FUT8 mRNA in the (F) T24 and (G) UM-UC-3 cell lines was detected by quantitative real-time PCR with actinomycin D treatment at the indicated time points. The relative expression of circFUT8 was normalized to the expression of 0 h. (H) The relative abundance of circFUT8 and FUT8 mRNA in T24 and UM-UC-3 cell lines was detected by quantitative real-time PCR with or without RNase R treatment. (I) Nuclear and cytoplasmic RNA fractionation experiment showed that circFUT8 was mainly localized in the cytoplasm, and the abundance of circFUT8 was normalized to the value measured in the cytoplasm. (J) FISH assay of the T24 cell line indicated that circFUT8 was mainly distributed in the cytoplasm. Nuclei were stained blue by DAPI. circFUT8, U6, and 18S rRNA were labeled with Cy3 and stained red. Scale bar, 50 μm. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three experiments. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, Student’s t-test.