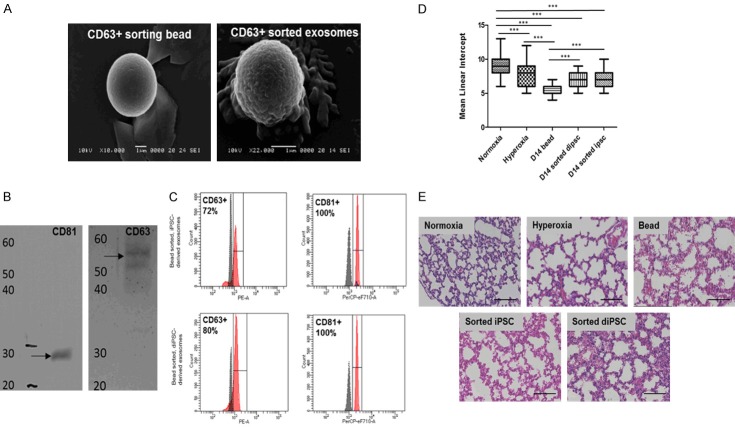
Figure 5.
Characterization of exosomes derived from iPSCs and diPSCs. A. SEM analysis of CD63 + sorting beads with and without exosomes. B. Western blot analysis of exosomes derived from iPSCs. Exosomes isolated with CD81 sorting beads were positive for both CD81 (MW: 28 kDa) and CD63 (MW: 55 kDa) surface markers. C. FACS analysis of exosomes derived from both iPSCs and diPSCs and bound to CD63 and CD81 sorted beads. iPSC derived exosomes were positive for CD63 and CD81 surface markers (72% and 100%, respectively). diPSC derived exosomes were positive for CD63 and CD81 surface markers (80% and 100%, respectively). D. Mean linear intercept values for mice administered diPSC and iPSC derived exosomes bound to beads. Across all groups the statistically significant differences were seen in normoxia vs. hyperoxia, P<0.001 normoxia vs. D14 bead, P<0.001 normoxia vs. D14 sorted diPSC, P<0.001 normoxia vs. D14 sorted iPSC, P<0.001 hyperoxia vs. D14 bead, P<0.001 D14 bead vs. D14 sorted iPSC, P<0.001 D14 bead vs. D14 sorted diPSC, P<0.001. P<0.01. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 between indicated groups. E. Representative H + E staining of all groups, each image has the MLI closest to the group mean, scale bars 50 µm.