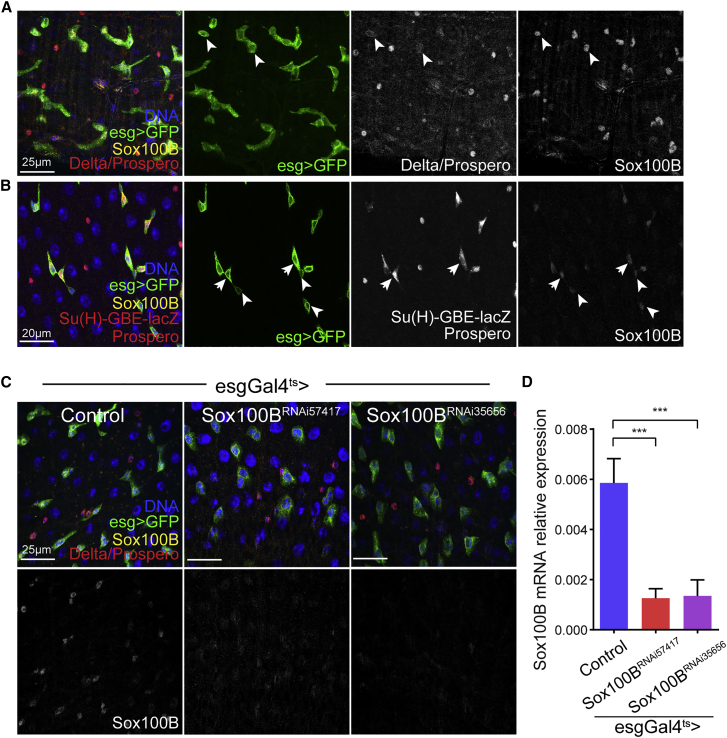
Figure 1.
Sox100B Is Expressed in ISCs and EBs in the Adult Intestine
(A and B) Representative confocal images of Sox100B expression in the adult posterior midgut showing that Sox100B is expressed in both Delta-positive ISCs––indicated by arrowheads in (A)––and EBs which have high Notch reporter activity––indicated by arrows in (B). Sox100B is not expressed in mature ECs and only marginally detected in a subset of EEs. ISC, intestinal stem cell; EB, enteroblast; EE, enteroendocrine; EC, enterocyte.
(C) Sox100B antibody staining is strongly reduced when two independent Sox100BRNAi (Bloomington TRiP stocks 57417 and 35656) were specifically expressed in the ISCs and EBs using the esgGal4ts driver for 6 days.
(D) qRT-PCR data demonstrates that Sox100B mRNA expression is strongly reduced in Sox100BRNAi -expressing ISCs and EBs after 7days knocking down. Sox100B mRNA expression is normalized to actin5c expression.
In (A–C) UAS-GFP expression driven by the esgGal4 labels both ISCs and EBs (green), DNA is stained by Hoechst (blue), Delta/Prospero/β-gal antibody staining (red) labels ISCs, mature EEs, and GBE-lacZ-positive EBs, respectively (Delta, membrane staining; Prospero, nuclear staining; GBE-lacZ, cytoplasmic staining). Scale bars, 25 μm (A and C) and 20 μm (B). In (D), values are presented as averages ± SEM of four independent biological replicates per condition; p values are calculated using unpaired two-tailed Student's t test; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.