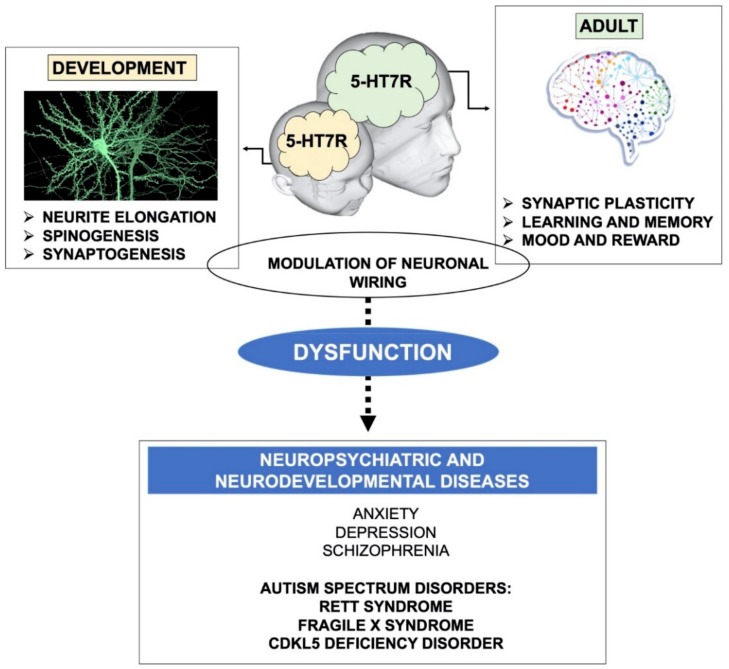
Figure 1.
Schematic drawing illustrating the role of the 5-HT7R in brain plasticity and connectivity. During development, the 5-HT7R contributes to proper neuronal wiring through the stimulation of neurite elongation, growth and maturation of dendritic spines, and synaptogenesis. During adulthood, the 5-HT7R signaling stimulates synaptic plasticity (LTP, LTD and structural remodeling of neuronal connections), which in turn affects many physiological functions, such as learning, memory, mood and reward. Dysregulated 5-HT7R signaling was demonstrated in neuropsychiatric and neurodevelopmental diseases characterized by altered brain connectivity. Notably, 5-HT7R stimulation exerts a widespread beneficial effect on behavioral and molecular alterations in various mouse models of Autism Spectrum Disorders (highlighted in bold).