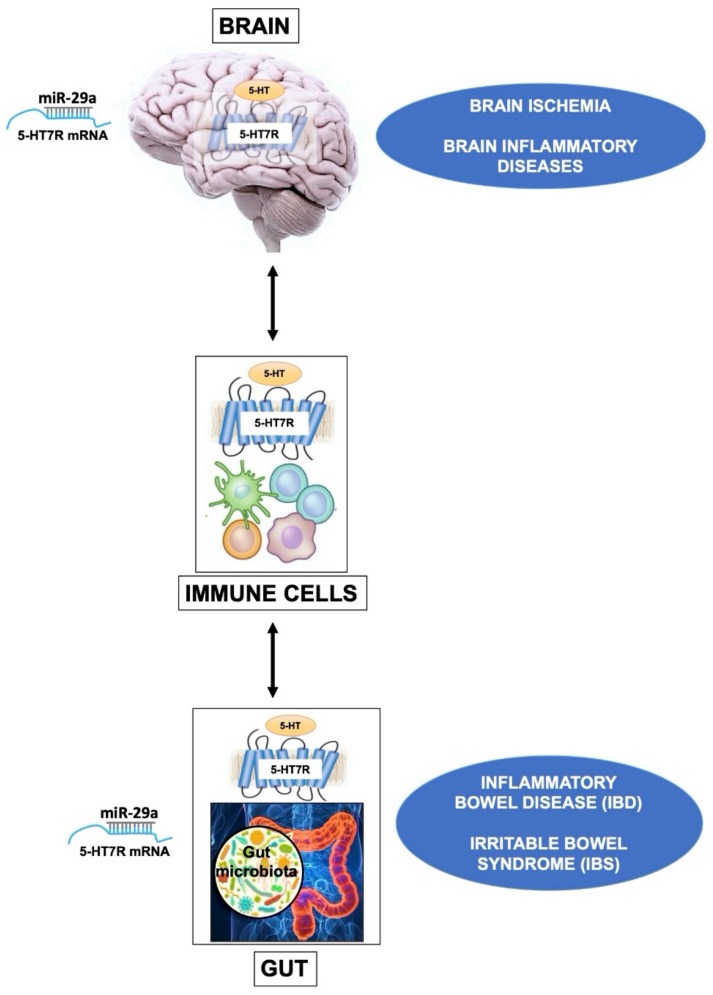
Figure 2.
The drawing outlines the influence of 5-HT7R in brain, gut and immune cells. In the CNS, the 5-HT7R expressed by brain Treg cells displays specialized functions that contribute to their proliferation after ischemic stroke, promoting neurological recovery. A similar mechanism is likely to occur also in other neuroinflammatory diseases. In immune cells, the basal activity of 5-HT7R is likely to play a key role in the maintenance of homeostasis. In the gut, alteration of the 5-HT metabolism is associated with various diseases such as Inflammatory Bowel Disease (IBD), and Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS). In these dysfunctions the activation of 5-HT7R on dendritic cells modulates their immune response, resulting in either beneficial or detrimental effects, depending on experimental models. It is worth to underline that the expression level of 5-HT7R is epigenetically modulated by the microRNA-29a (miR-29a) in the brain as well as in the gut.