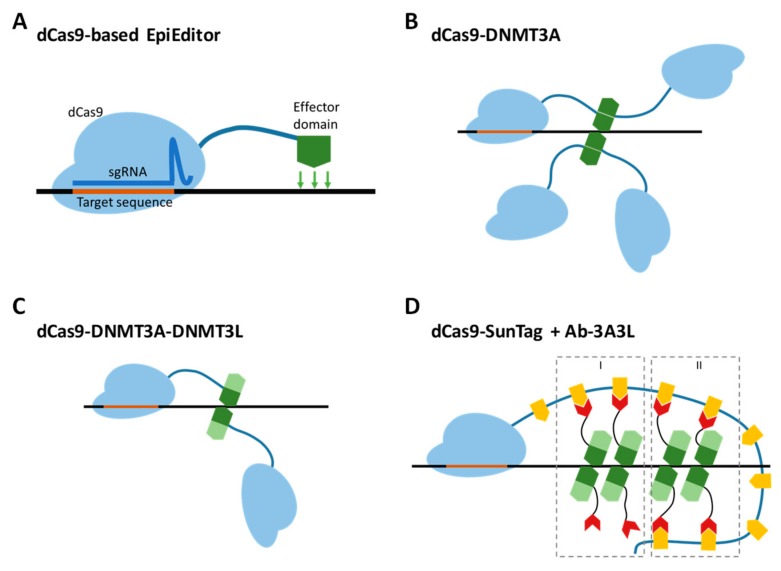
Figure 1.
EpiEditors for targeted DNA methylation. (A) General design of an EpiEditor containing a chromatin-modifying enzyme (effector module, green) fused to a catalytically deactivated Cas9 protein (dCas9, light blue) in complex with a single guide RNA (sgRNA, dark blue) complementary to the target genomic locus. (B) The direct fusion protein of dCas9 and the C-terminal domain of DNMT3A form a tetramer at a target site to produce a catalytically active complex. (C) The dCas9 direct fusion protein with the fused C-terminal domains of DNMT3A (dark green) and DNMT3L (light green) form an active complex by dimerization. (D) Co-expression of two chimeric proteins, dCas9-SunTag and Ab-3A3L (containing the fused C-terminal domains of DNMT3A and DNMT3L, dark and light green), leads to the formation of active complexes by dimerization of recruited and free Ab-3A3L (mechanism I) or only by interaction of two recruited Ab-3A3L dimers (mechanism II). The orange shapes represent the GCN4 peptide sequence, the red shapes represent the scFv antibody binding to the GCN4 peptide.