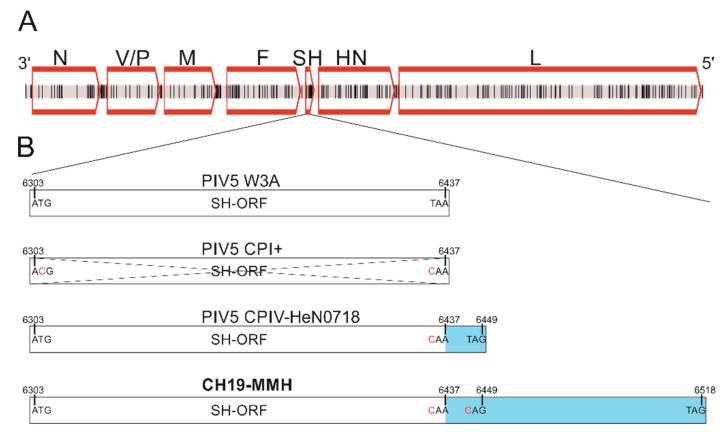
Figure 1.
Schematic presentation of the PIV5 CH19-MMH genome and comparison to other PIV5 strains. (A) Nucleotide differences to the closest related PIV5 strain H221 are marked as black vertical lines. Open reading frames (ORFs) are indicated by red boxes. N: nucleocapsid protein, V: V-protein, P: phosphoprotein, M: matrix protein, F: fusion protein, SH: small hydrophobic protein, HN: hemagglutinin-neuraminidase protein, L: large protein. (B) The open reading frame of the SH protein (SH-ORF) varies in published full-length PIV5 genomes. In most strains, the SH-ORF is 132 bp long (exemplarily shown with strain W3A). In some strains, the start as well as the stop codon is mutated (exemplarily shown with strain CPI+) so that the gene is not probably transcribed. In two strains, a mutation in the stop codon is described, leading to a 12 bp longer ORF (exemplarily shown with strain CPIV-HeN0718). In the sequenced PIV5 CH19-MMH genome of this study, two stop codons are mutated, suggesting an 81 bp longer ORF. Numbers stand for the nucleotide position in the PIV5 genome, letters stand for bases, and red letters indicate mutated bases compared to the PIV5 reference strain. ORFs are depicted by boxes, the crossed-out box indicates a missing ORF, and the blue color indicates the ORF elongations.