Figure 4.
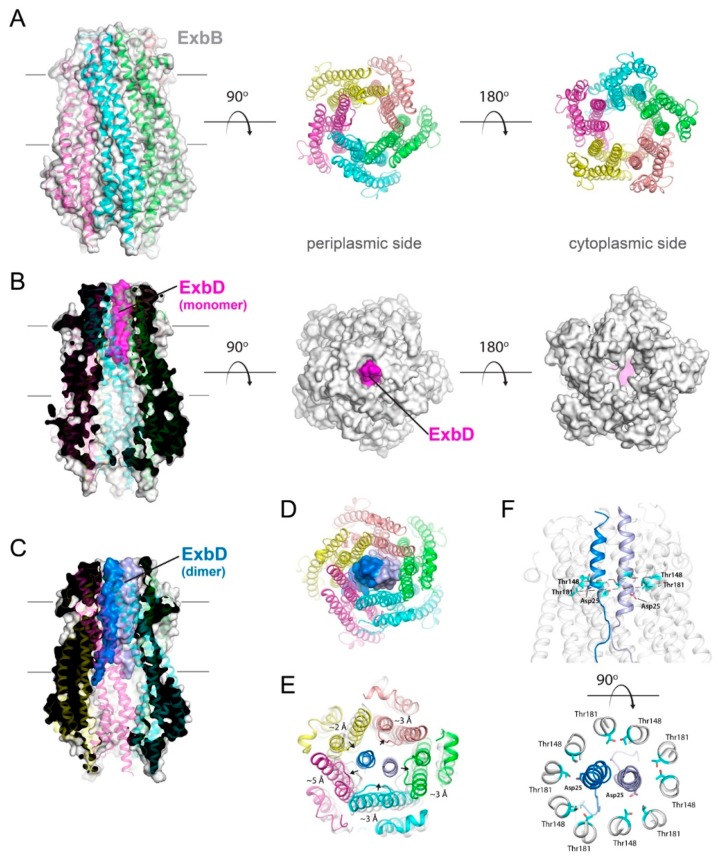
Structures of the pentameric ExbB/D subcomplex. (A) The X-ray structure of the ExbB/ExbD subcomplex (PDB ID 5SV0) shown in ribbon and surface. Here, ExbB is a pentamer which has pseudo 5-fold symmetry on the periplasmic side and 5-fold symmetry on the cytoplasmic side. In this structure, solved at neutral pH, ExbD was mostly disordered and missing in the electron density. A cryoEM structure of the pentameric form of ExbB was also recently reported (PDB ID 5ZFV). (B) The X-ray structure of the ExbB/ExbD subcomplex (PDB ID 5SV1) at low pH. In this structure, the transmembrane helix for ExbD (magenta) was observed inside the pore of the ExbB pentamer and offset from the plane of the membrane, as shown in the cutaway representation on the left panel. (C) The cryoEM structure (PDB ID 6TYI) showing a dimeric form of ExbD sitting within the pentameric pore of ExbB. (D) A view of the cryoEM structure from panel C looking down the pore from the periplasmic side. The ExbD dimer is in surface with each chain in a different shade of blue. (E) The same view as in panel D, but depicting the conformational changes observed in ExbB to accommodate the ExbD dimer. The structure from panel A is shown in gray for comparison and the subunit shifts are indicated by the black arrows and approximate measurements noted. (F) The cryoEM structure from panel C showing the locations of the conserved residues in ExbB (Thr148 and Thr181) and ExbD (Asp25) that are proposed to play a role in proton transport from the pmf for energy production. A side view is shown in the top panel while a top down view is shown in the bottom panel.