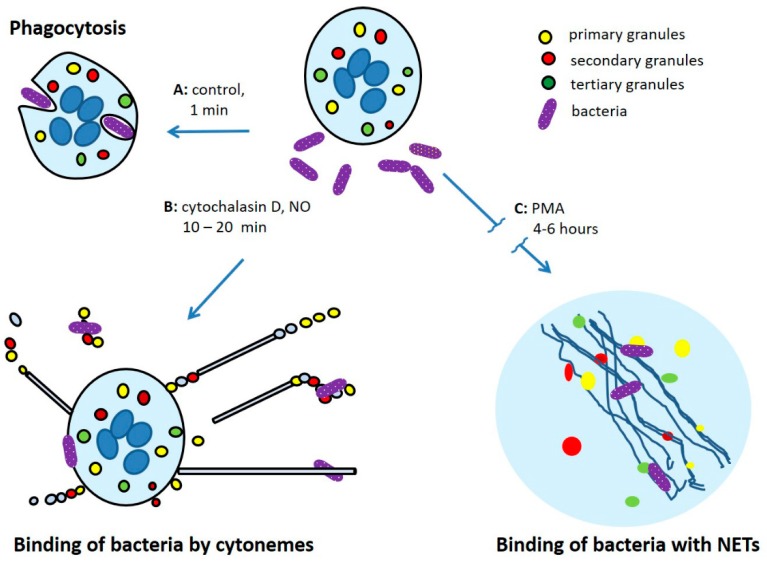
Figure 1.
Mechanisms of interactions of human neutrophils with bacteria: (A) phagocytosis; (B) extracellular binding of bacteria by cytonemes of living neutrophils; (C) binding of bacteria by neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) composed of nuclear DNA and granular proteins released by dead neutrophils.