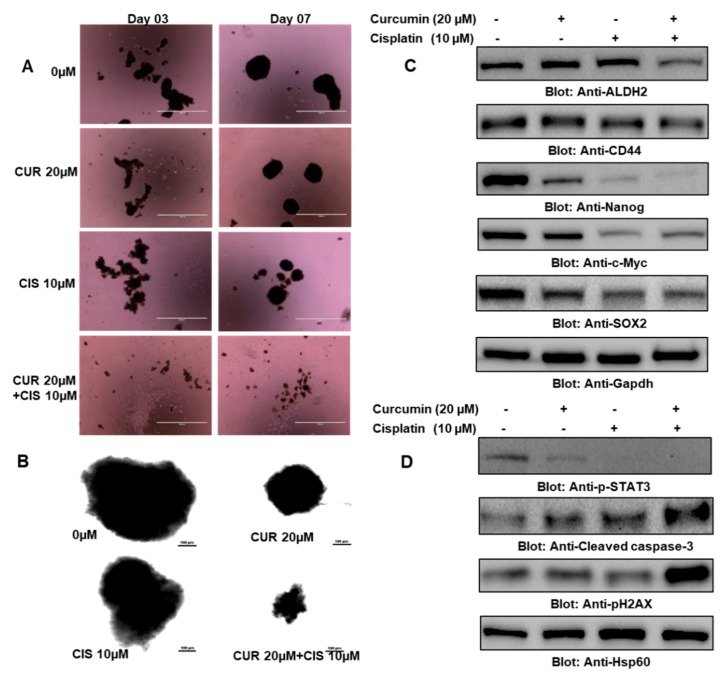
Figure 9.
Cotreatment of curcumin and cisplatin potentiated the inhibition of cancer stem cell (CSC) growth and stemness features. (A) Treatment with curcumin and cisplatin inhibited thyrosphere formation. BCPAP cells were grown and treated in ultralow attachment plates with 0 µM or 20 µM of curcumin and 10 µM of cisplatin alone and in combination for 7 days, and images of thyrospheres were taken on day 3 and day 7 using an EVOS FLc Cell Imaging System from Invitrogen (Thermo Fisher Scientific) at a magnification of 4×(scale bar 1000 µm). (B) BCPAP cells were grown and treated in ultralow attachment plates with 0 µM and 20 µM of curcumin and 10 µM of cisplatin alone and in combination for 7 days, and images of thyrospheres were taken on day 7 through a confocal microscope at a magnification of 20×(scale bar 100 µm). (C) Cotreatment of curcumin and cisplatin potentiated the inhibition of stemness features in PTC cells. Thyrospheres were grown and treated in ultralow attachment plates with 0 µM or 20 µM of curcumin and 10 µM of cisplatin alone and in combination, followed by cell lysis and western blotting against ALDH2, CD44, Nanog, c-Myc, SOX-2, and Gapdh. (D) Cotreatment with curcumin and cisplatin potentiated the apoptosis of CSCs. Thyrospheres were grown and treated in ultralow attachment plates with 0 µM and 20 µM of curcumin and 10 µM of cisplatin alone and in combination for 7 days, followed by cell lysis and western blotting against p-STAT3, cleaved caspase-3, p-H2AX, and Hsp60. CUR: curcumin; CIS: cisplatin.