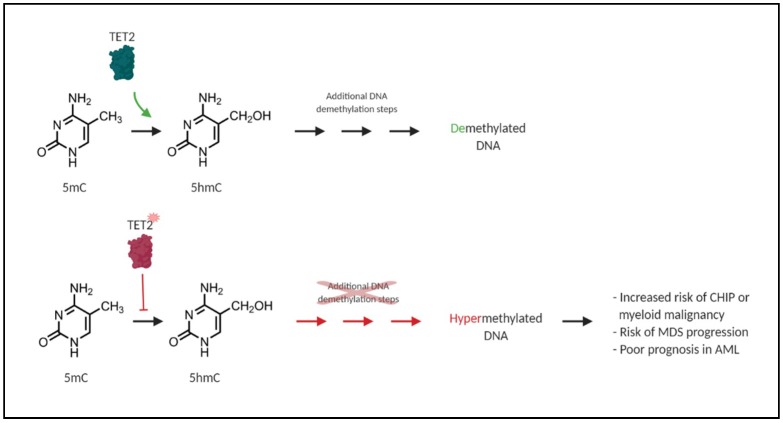
Figure 2.
Loss-of-function mutations in TET2 result in DNA hypermethylation. TET2 is an alpha-ketoglutarate- and Fe2+-dependent dioxygenase (α-KGDD) that catalyzes the oxidation of 5-methylcytosine (5mC) to 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC). This is a required step in proper DNA repair and DNA demethylation (green). Loss-of-function mutations in TET2 in CHIP and myeloid malignancies disrupt this oxidation step and result in a general DNA hypermethylation phenotype (red) and aberrant HSPC self-renewal, which is associated with an increased risk of CHIP, myeloid malignancy, MDS progression, and poor prognosis in AML [35].