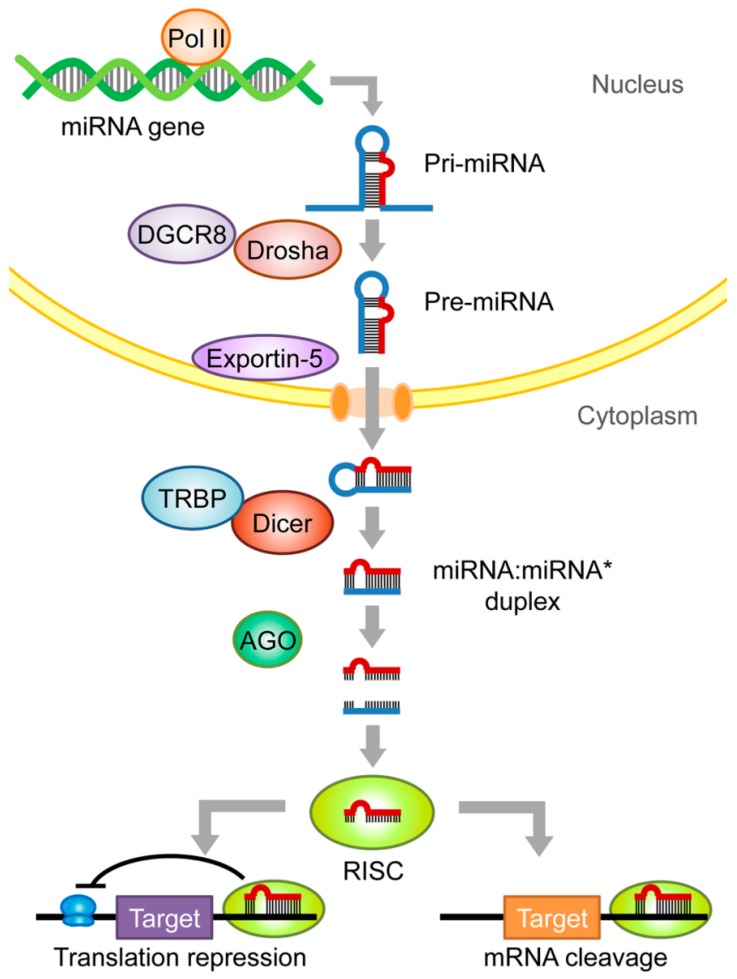
Figure 1.
MicroRNA (miRNA) biogenesis. This schematic diagram illustrates the canonical pathway of miRNA biogenesis. The miRNA gene is transcribed by RNA polymerase II (Poly II) to generate the primary miRNA (pri-miRNA) that forms hairpin structures. The long pri-miRNA is then processed by Drosha and DiGeorge syndrome critical region 8 (DGCR8) into the shorter precursor miRNA (pre-miRNA), which is then exported to the cytosol with the help of exportin-5. The pre-miRNA is further cleaved by Dicer and transactivation response element RNA-binding protein (TRBP), yielding the miRNA:miRNA* duplex molecule, which is loaded into argonaute (AGO) to unwind and form the functional RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC). The mature miRNA then binds to the seed sequences on the 3′ untranslated region (3′UTR) of the target mRNA, leading to its translation repression or cleavage and thereby degradation.