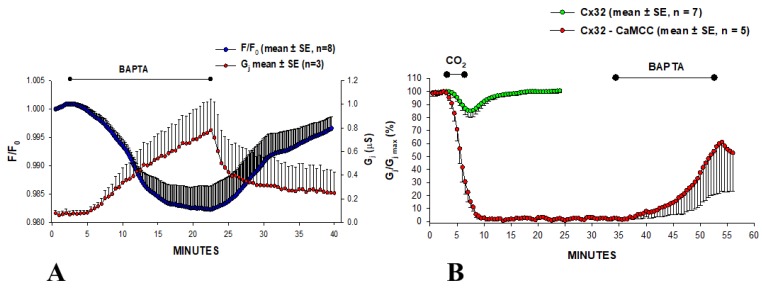
Figure 6.
Junctional conductance (Gj) and Ca2+i (A) monitored in Xenopus oocyte pairs expressing Cx32. In oocytes expressing CaMCC, Gj is very low, but it dramatically and reversibly increases when [Ca2+]i is lowered with 180 µM BAPTA superfusion (A). This indicates that CaMCC greatly increases Ca2+-gating sensitivity, such that even basal [Ca2+]i affect gating. This was confirmed by testing the effect of CO2 (B). With 3 min exposure to 100% CO2, Gj rapidly drops to zero, whereas in controls it decreases by only ~15% (B); Gj remains at 0 indefinitely, but recovers (reversibly) with 180 µM BAPTA application (B). Adapted from Reference [107].