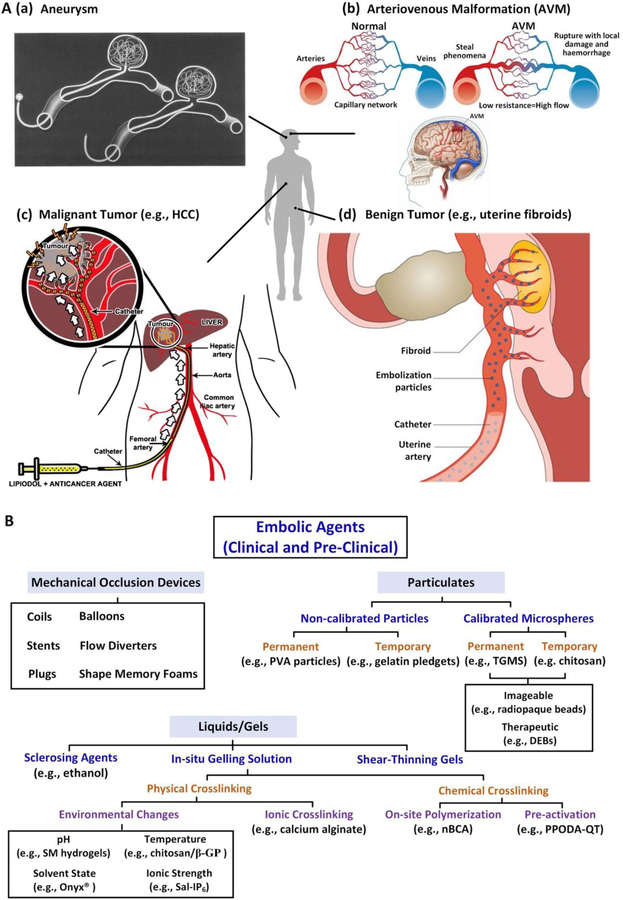
Figure 1.
A) Schematic demonstrating embolization of (a) aneurysms; (b) AVMs; (c)malignant tumors (e.g., hepatocellular carcinoma, HCC) and (d) benign tumors (e.g., uterine fibroids). Figure components adapted and reproduced with permission.[12] Copyright 2000, Elsevier; 2014, BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.; 2015 Springer Nature; 2013, Elsevier; and 2016, Springer Nature. B) Summary of clinical and pre-clinical embolic agents. PVA: polyvinyl alcohol; TGMS: trisacryl gelatin microspheres; DEB: drug eluting bead; SM: sulfamethzaine; β-GP: β-glycerophosphate; Sal: polycationic salmine sulfate; IP6: polyanionic sodium inositol hexaphosphate; nBCA: N-bnutyl-2-cyanoacrylate; PPODA: poly(propylene glycol) diacrylate; QT: pentaerythritol tetrakis 3-mercaptopropionate.