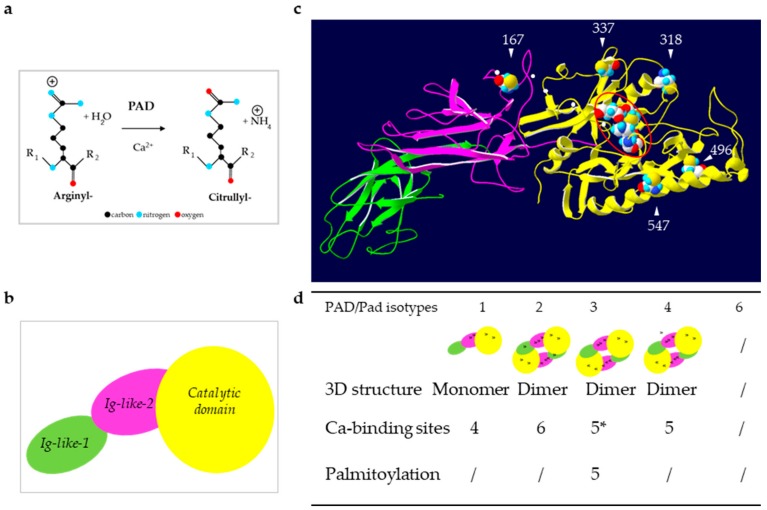
Figure 1.
Reaction of deimination and structure of PADs. (a) Schematic representation of the reaction catalyzed by PADs: Deimination or citrullination. (b) Schematic representation of the sub-domains of PADs. (c) Illustration of an in silico three-dimensional (3D) model of the active PAD3. The white arrowheads indicate the five putatively palmitoylated cysteines (by similarities to mouse Pad3). The small white dots indicate the five conserved calcium binding sites. The four gathered major amino-acids of the active site are highlighted by a red oval (Asp350, His470, Asp472 and Cys646 by similarities to PAD4). (d) Summary of the structural data for each human (PAD) and mouse (mPad) isotypes. Positions of the calcium binding sites are indicated by black dots on each sub-domain representation. * As observed after a multiple sequence alignment (MultAlin), the amino-acids involved in the five calcium binding sites are highly conserved, especially between PAD4 and PAD3 [13]. / means that the information is not known.