Fig. 2. The mutant MAPK8 allele is loss-of-expression.
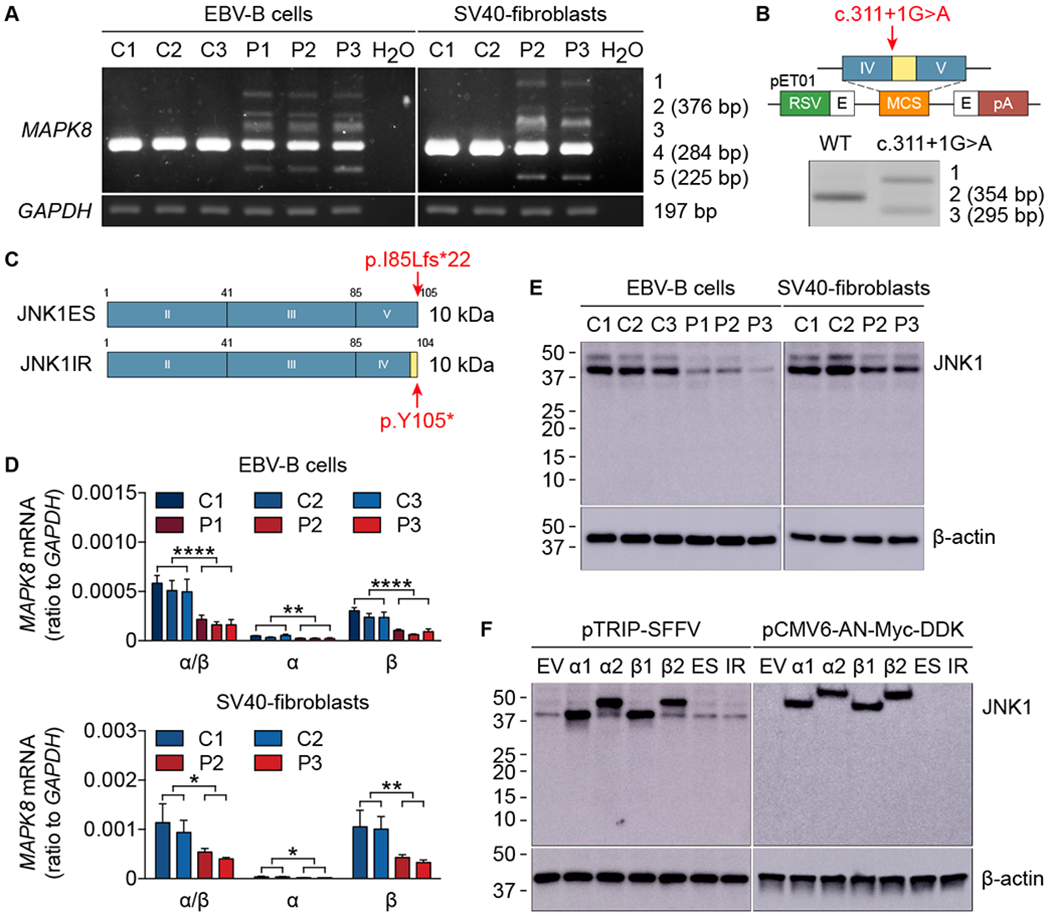
(A) MAPK8 mRNA levels in EBV-B cells and SV40-fibroblasts from healthy controls (C1, C2, and C3) and patients (P1, P2, and P3). TA cloning and subsequent sequencing of the five bands generated by amplification from exon III to exon V identified three spliced transcripts: band 1 corresponding to the WT sequence together with intron IV retention and exon IV skipping; band 2 (376 bp) corresponding to intron IV retention; band 3 corresponding to the WT sequence together with exon IV skipping; band 4 (284 bp) corresponding to the WT sequence; band 5 (225 bp) corresponding to exon IV skipping. (B) Schematic diagram of the constructs used for exon trapping. pET01, exon-trapping vector; RSV, Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat promoter; pA, polyadenylation; E in black, exon of the pET01 vector; IV and V in blue, MAPK8 exons IV and V; in yellow, MAPK8 intron IV. The red arrow indicates the position of the mutation. RT-PCR and subsequent sequencing identified three spliced transcripts: band 1 corresponding to intron IV retention and exon IV skipping; band 2 (354 bp) corresponding to the WT sequence; band 3 (295 bp) corresponding to exon IV skipping. (C) Schematic illustration of the mutant proteins. JNK1ES (JNK1 exon skipping) represents exon IV skipping, whereas JNK1IR (JNK1 intron retention) denotes intron IV retention. Both transcripts are predicted to encode proteins of approximately 10 kDa in size. Red arrows indicate the positions of premature stop codons. (D) mRNA levels for MAPK8 isoforms in EBV-B cells (top panel) and SV40-fibroblasts (bottom panel) from healthy controls (C1, C2, and C3) and patients (P1, P2, and P3). Quantitative RT-PCR was performed with primers specific for JNK1α1/JNK1α2 and JNK1β1/JNK1β2 mRNAs. α/β, total mRNA corresponding to JNK1α1, JNK1α2, JNK1β1, and JNK1β2; α, total mRNA corresponding to JNK1α1 and JNK1α2; β, total mRNA corresponding to JNK1β1 and JNK1β2. The values shown are the means ± SEM of three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01, and ****, P < 0.0001; in unpaired t tests. (E and F) Immunoblot of JNK1 in EBV-B cells and SV40-fibroblasts from healthy controls (C1, C2, and C3) and patients (P1, P2, and P3) (E), and in HEK293T cells transfected with plasmids encoding four WT JNK1 isoforms (α1, α2, β1, and β2) and two mutants (ES and IR) inserted into the pTRIP-SFFV vector or the pCMV6-AN-Myc-DDK vector (F). Endogenous JNK1 was detected with an anti-JNK1 antibody recognizing the N-terminus of JNK1. Myc-tagged JNK1 was detected with an anti-Myc antibody. EV, empty vector. The data shown are representative of three independent experiments (A, B, E, and F).
