Fig. 6. JNK1-dependent IL-17 and TGF-β signaling.
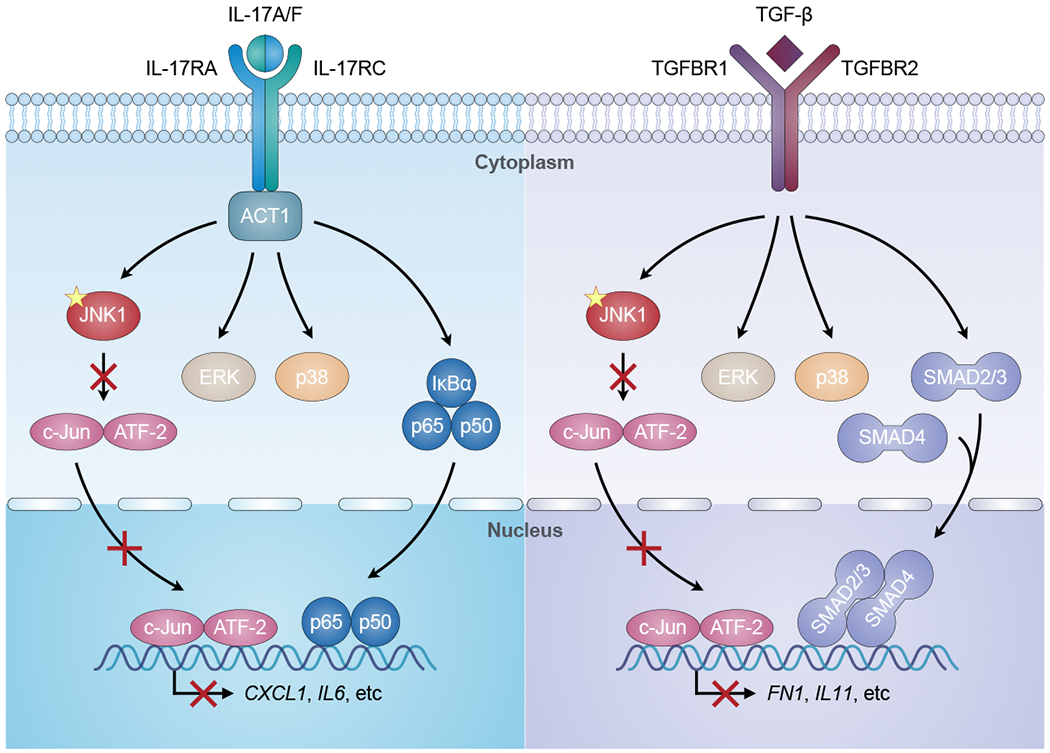
The binding of IL-17A/F to the IL-17RA/IL-17RC receptor facilitates the recruitment of ACT1 to the receptor, which mediates the activation of JNK1, ERK, p38, and NF-κB (p65/p50) signaling, leading to the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines (e.g. CXCL1, IL6). Similarly, TGF-β binds to its receptor (TGFBR1/TGFBR2), leading to the activation of JNK1, ERK, p38, and SMAD (SMAD2/3/4) signaling. This pathway ultimately results in the production of extracellular matrix proteins and regulators (e.g. FN1, IL11). The mutation (yellow star) in JNK1 impairs the JNK1-dependent activation of downstream AP-1 (c-Jun/ATF-2), thereby reducing the JNK1-dependent cellular responses to IL-17 and TGF-β.
