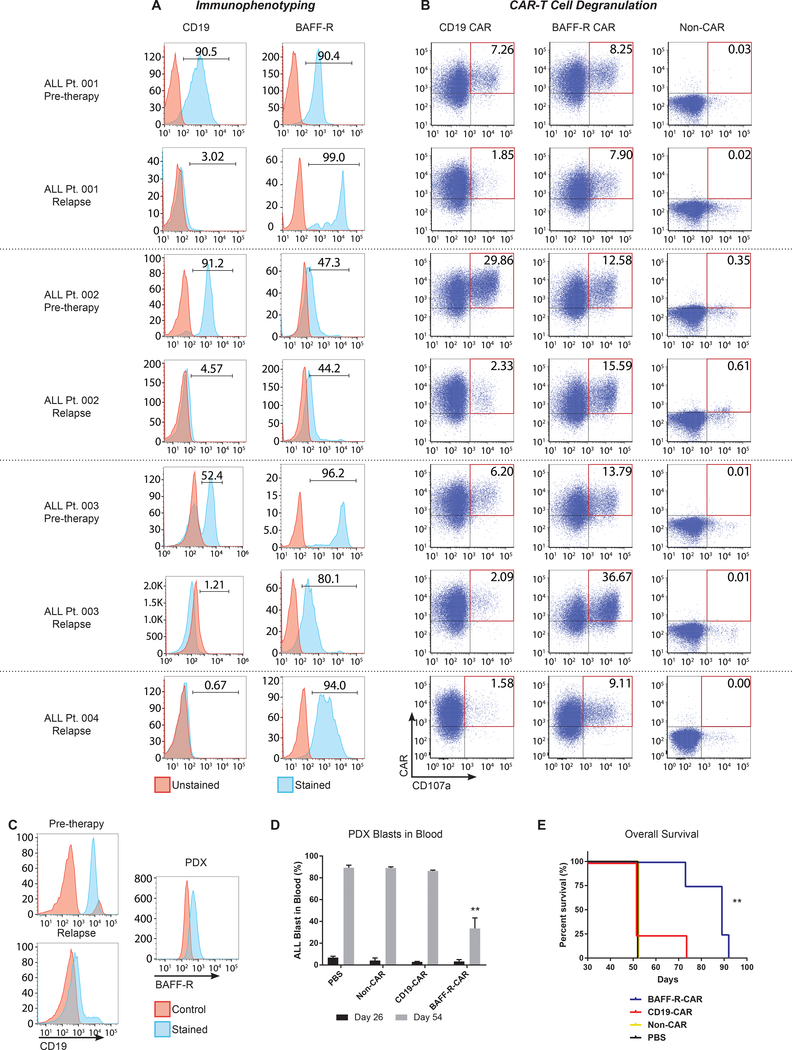
Figure 6. BAFF-R specific activation of CAR T cells by primary CD19 antigen-loss human ALL escape variants and antitumor effects of CAR T cells in vivo.
Blood or bone marrow tumor samples were obtained from ALL patients relapsing with CD19-negative tumors following CD19 bi-specific antibody treatment (relapse) and analyzed together with each patient’s corresponding pre-therapy tumor. (a) FACS histograms showing expression of CD19 and BAFF-R. (b) Cryopreserved ALL samples were co-cultured with BAFF-R or CD19 CAR-T cells derived from a single healthy donor in the presence of anti-CD107a antibody for 6 h. Non-transduced T cells (non-CAR) from a single donor were used as a negative control. (c) FACS analysis of CD19-negative B-ALL cells isolated at relapse from a fifth patient for PDX establishment. B-ALL cells (106 cells/mouse) were injected into NSG mice, and 4 mice/group were then randomly assigned to treatments of BAFF-R-or CD19-CAR T cells (5 × 106, 1:1 CD4:CD8 TN CAR T cells ratio/mouse) on day 26. Non-transduced T cells (1:1 CD4:CD8 TN cells) from the same donor were used as allogeneic controls (non-CAR) (d) Percentage of peripheral blood CD19-negative B-ALL blasts in PDX mice at days 26 and 54. B-ALL blasts were identified by CD45+CD22+CD58+ staining. Two-way, repeated measures ANOVA and Sidak’s multiple comparisons test: **P<0.001 BAFF-R CAR vs. CD19-CAR and controls. (e) Overall survival of CD19-negative B-ALL PDX mice after BAFF-R CAR-T treatment. Control groups include CD19 CAR-T, non-transduced T cells, and PBS. Log-rank test: **P<0.01 vs. CD19-CAR, non-CAR, and PBS control.