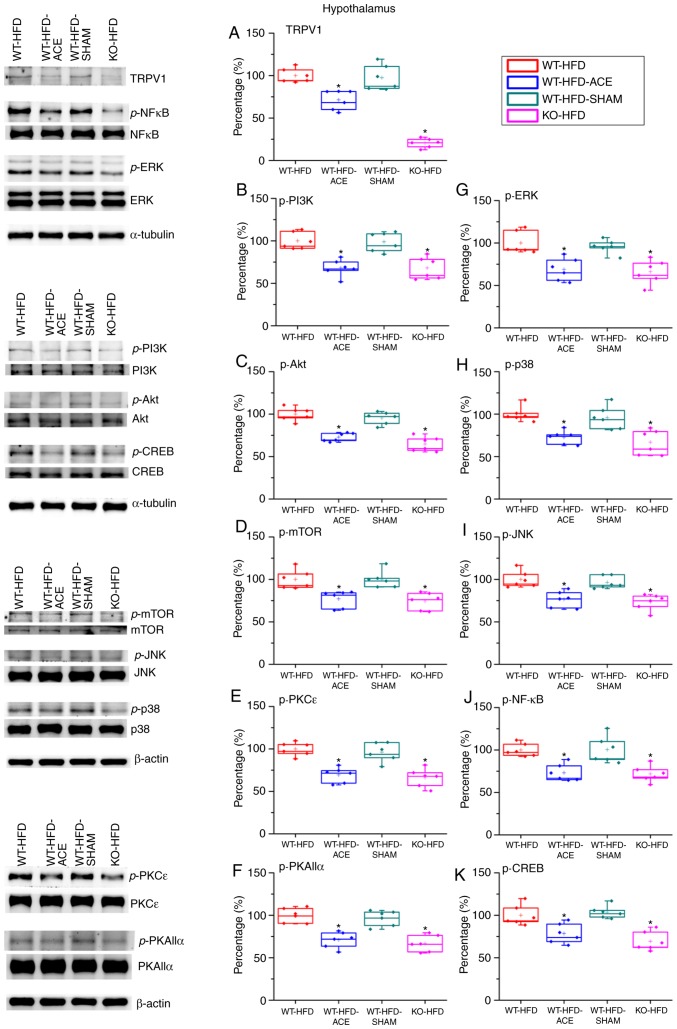
Figure 4.
Expression levels of TRPV1 and associated molecules in the hypothalamus. The expression pattern of TRPV1 protein was detected in the following groups: WT-HFD; WT-HFD-ACE; WT-HFD-SHAM; and KO-HFD. The results revealed significant increases in (A) TRPV1, (B) p-PI3K, (C) p-Akt, (D) p-mTOR, (E) p-PKCε, (F) p-PKAIIα, (G) p-ERK, (H) p-p38, (I) p-JNK, (J) p-NF-κB and (K) p-CREB expression levels in the WT-HFD and WT-HFD-SHAM groups compared with the other groups (*P<0.05). These increases were statistically decreased in the WT-HFD-ACE group that received ACE treatment and in the KO-HFD group that lacked the TRPV1 receptor. *P<0.05. TRPV1, transient receptor vanilloid member 1; WT, wild-type; ND, normal diet; HFD, high-fat diet; ACE, acupoint catgut embedding; KO, knockout; p, phosphorylated; PKCε, protein kinase C epsilon type; PKAIIα, protein kinase AII α; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; p38, p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; CREB, cyclic AMP-response element binding protein.