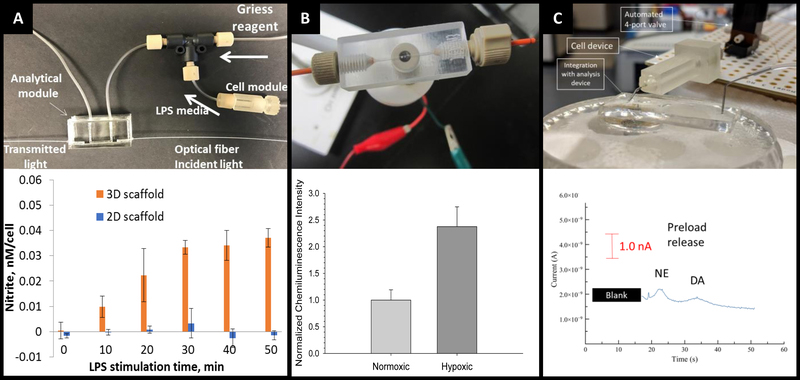
Figure 15:
3D printed devices as a mechanism for cell culture and analysis. (A) A 3D printed cell culture module with fiber scaffold inserts is connected to a PDMS-based optical flow cell. Using this set up nitrate from macrophages was quantified. It was determined that macrophages on 3D scaffolds better mimic the in vivo M1 state. (Adapted from Ref 24 with permission from Springer Nature) (B) A 3D printed electrochemical flow cell with threaded inlet and outlet for easy capillary connections. Using these threaded electrodes the researchers were able to confirm normoxic or hypoxic conditions in flowing red blood cells while simultaneously measuring ATP release with the luciferin/ luciferase assay. (Adapted from ref 39 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry) (C) A 3D printed cell culture module is interfaced with PDMS chip by flow matching the solution being pushed through the cell culture module and the fluid being pulled through the PDMS chip. Using this technique, a 3D printed cell culture module could be coupled with a PDMS-based electrophoresis chip with electrochemical detection to separate and quantify norepinephrine and dopamine release from PC12 cells. (Adapted from ref 41 with permission from The Royal Society of Chemistry)