Figure 1. FcγRIIB Is Upregulated on FDCs during GC Responses, but It Does Not Affect GC B Cell Frequencies in 564Igi Mixed BM Chimeras.
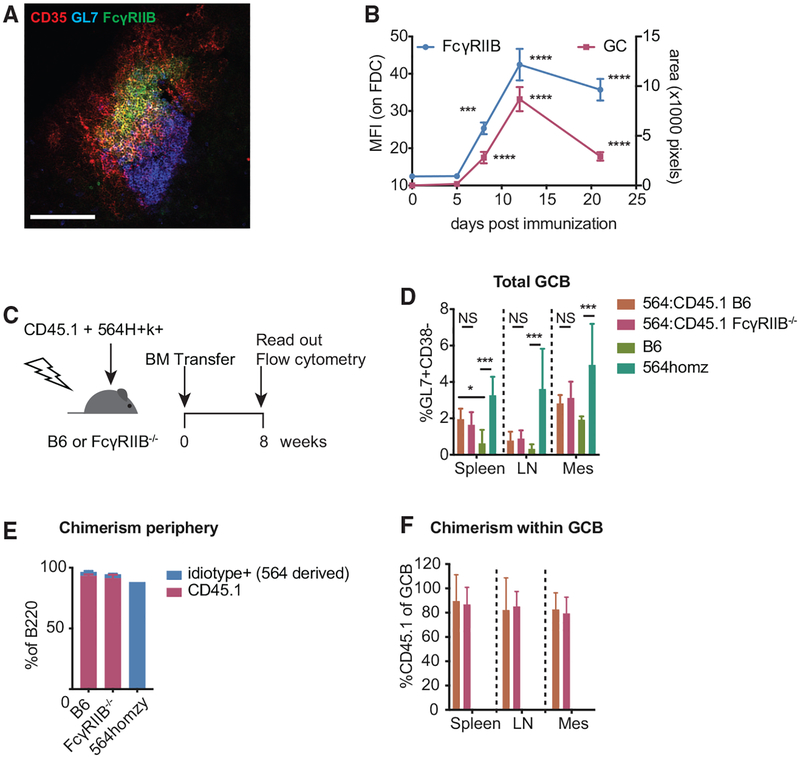
(A) Cropped confocal micrograph of a cryosection from a B6 popliteal lymph node 12 days after immunization with NP-CGG/alum. FDC networks are shown in red (CD35), FcγRIIB in green, and GC B cells in blue (Gl7). Scale bar, 100 μm.
(B) FcγRIIB staining on FDC networks and GC size at various days post-immunization. FcγRIIB mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) was measured within FDC masks as defined by CD35 staining. GC size was determined by GL7 staining associated with FDC networks. The absence of GL7 staining near FDCs was scored as an area of zero pixels. Each point contains at least 20 FDC networks from a total of 3–4 mice per time point. ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001, Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc testing, tested versus day 0. Error bars represent SEMs.
(C) Experimental setup of 564Igi mixed BM chimeras. BM cells harvested from CD45.1 and 564Igi homozygous mice were transferred (2:1 ratio) to age-matched, lethally irradiated B6 or FcγRIIB−/− recipients. Eight weeks post-transfer, GC frequency and chimerism were assessed by flow cytometry.
(D) GC B cell frequencies in spleen, inguinal lymph nodes (LNs) and mesenteric lymph nodes (mes) of chimeras, and naive B6 and 564Igi homozygous mice as measured by the frequency of GL7+CD38lo cells within B220 gated lymphocytes. n = 5 mice for B6 recipients and 7 mice for FcγRIIB−/− recipients. Kruskal-Wallis with Dunn’s post hoc testing, tested for each tissue separately. Error bars represent SDs.
(E) Chimerism in peripheral blood in B6 and FcγRIIB−/− recipients showing the percentage of B cells derived from 564Igi BM (anti-idiotype+, in blue) and B cells derived from CD45.1 BM (red). Also shown is the idiotype frequency in a 564Igi homozygous mouse to indicate the idiotype baseline frequency. Error bars represent SDs.
(F) Frequency of CD45.1 BM-derived cells within GC B cells. Error bars represent SDs.