FIGURE 1.
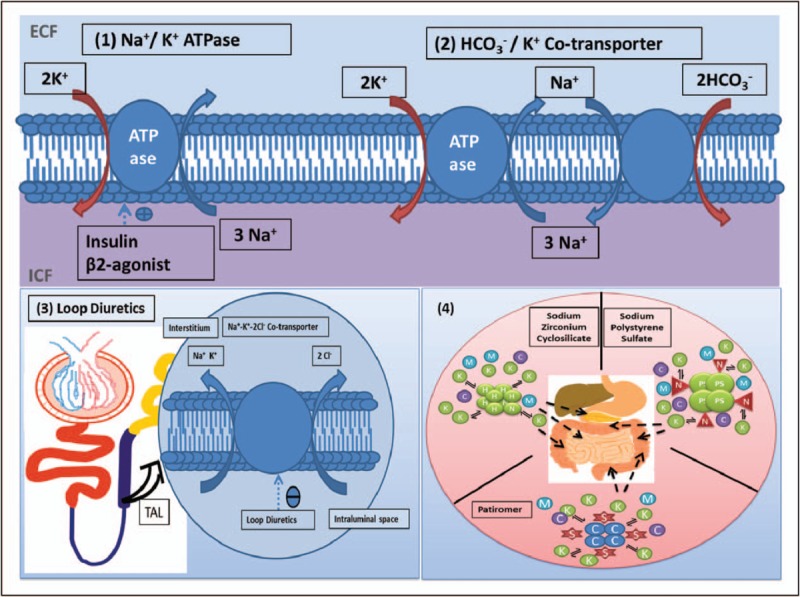
Mechanism of action of drugs for hyperkalemia. C, calcium; H, hydrogen; K, potassium; M, magnesium; N, sodium; S, sorbitol; TAL, thick ascending limb. (a) Shift K+ into cells. (1) Insulin and β2 agonists both stimulate the Na+/K+ ATPase facilitating extracellular potassium exchange for intracellular sodium. (2) Sodium bicarbonate stimulates the HCO3−/K+ cotransporter facilitating HCO3− and K+ cotransport in exchange for intracellular sodium. (b) Enhance K+ removal. (3) Via urine: Loop diuretics act on the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle inhibiting the Na+–K+–2Cl− cotransporter resulting in decreased sodium and potassium reabsorption. (4) Via gastrointestinal lumen: sodium zirconium cyclosilicate, patiromer and sodium polystyrene sulfate work by binding K+ in exchange for hydrogen, calcium and sodium (respectively) in the gastrointestinal lumen, allowing more potassium excretion.
