Figure 2.
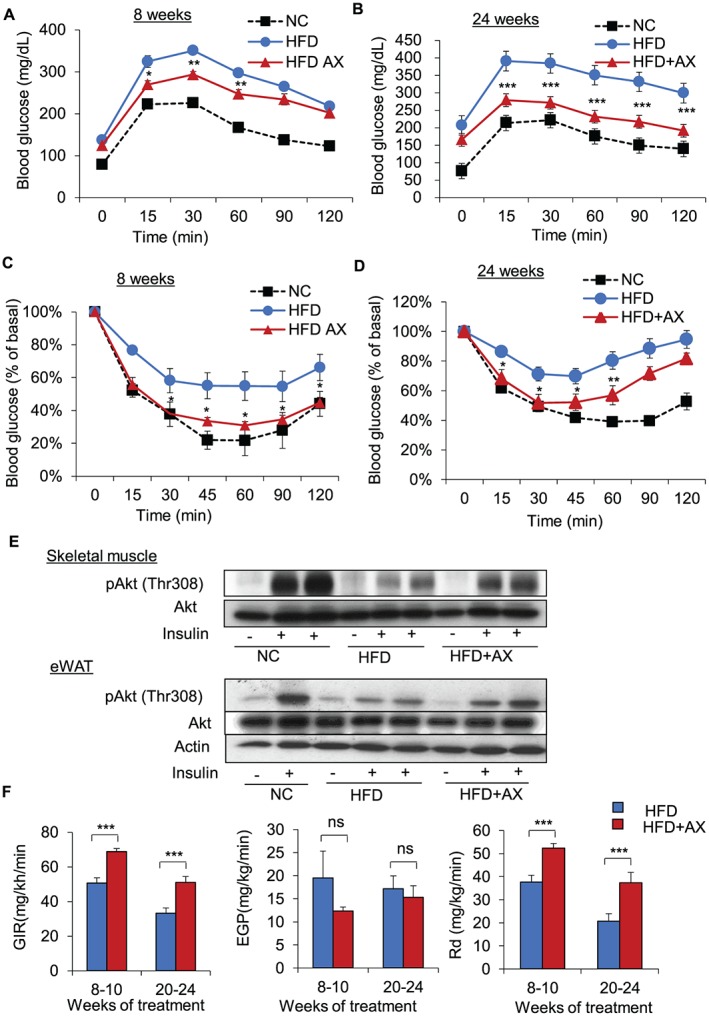
AX ameliorated the development of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance in lean and obese mice. (A,B) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (IP‐GTT) and (C,D) Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (IP‐ITT) in the AX‐treated HFD mice compared with control HFD and NC mice for 8 (A,C) or 24 weeks (B,D) (n = 5–9 per group). (E) Western blot analysis of insulin‐induced phosphorylation of Akt in the skeletal muscle or epididymal white adipose tissue (eWAT). (F) Glucose infusion rate (left), endogenous glucose production (EGP) or HGP (middle), and the rates of glucose disposal (Rd) (right) during the hyperinsulinemic‐euglycemic clamp study in the mice fed HFD or HFD+AX for 8–10 or 20–24 weeks (n = 6‐9 per group). All values are represented as means ± S.E.M. *p < 0.05 (HFD vs. HFD+AX). Statistical tests were performed as follows: (A, B; IP‐GTT and C, D; IP‐ITT) two‐way repeated‐measures ANOVA, and (F) Student's t‐test.
