Figure 4.
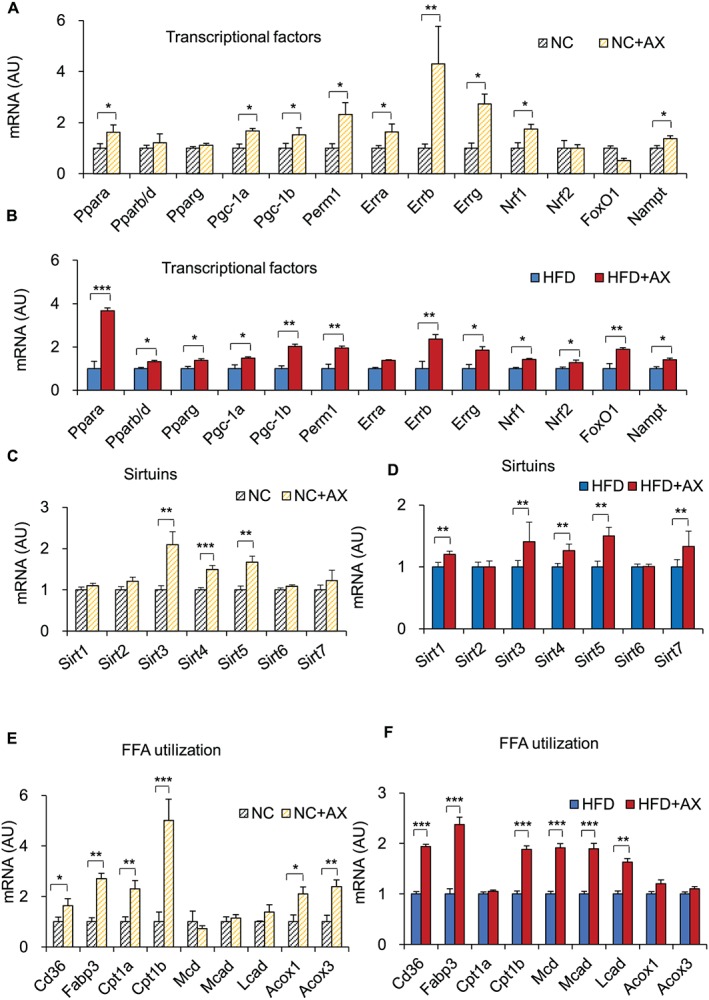
AX improved fatty acid utilization in the skeletal muscle through activation of mitochondrial function. Gene expressions in the gastrocnemius skeletal muscle relative to that of β‐actin expression, including of transcription factors related to mitochondrial energy metabolism‐related transcription factors in AX‐treated NC mice compared with the control NC mice (A) and AX‐treated HFD mice compared with control HFD mice (B), Sirtuin genes of the gastrocnemius muscle in AX‐treated NC mice compared with the control NC mice (C) and AX‐treated HFD mice compared with control HFD mice (D), FFA transport/β‐oxidation in AX‐treated NC mice compared with the control NC mice (E) and AX‐treated HFD mice compared with control HFD mice (F) (n = 6 per group). All values are presented as the means ± S.E.M.*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (HFD vs. HFD+AX) or (NC vs. NC+AX). Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t‐test.
