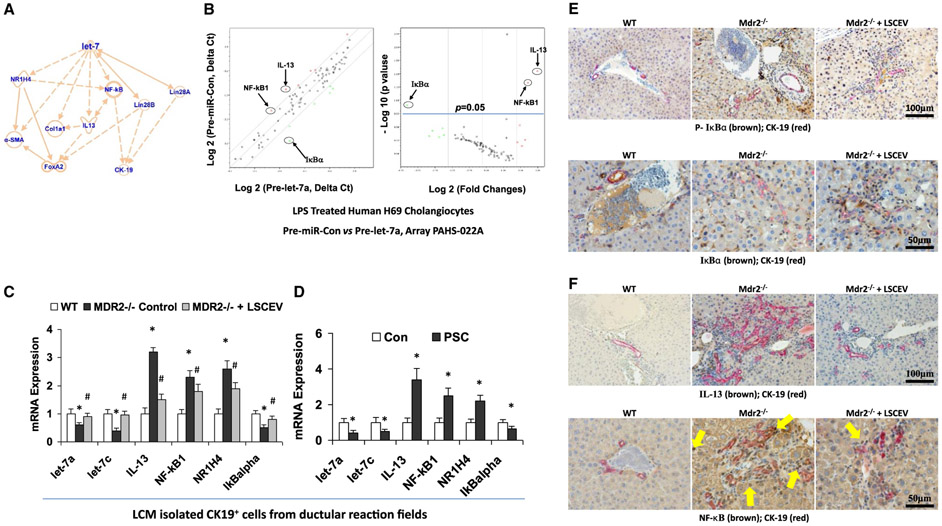
FIG. 6.
Let-7 associated anti-inflammation and antifibrosis signaling mechanisms in LSCEV-treated H69 cells and MDR2 −/− mice liver. (A) IPA based on LSEC treatment in MDR2 −/− mice and miRNA PCR array discoveries showed that let-7 may target IL-13/NR1H4/NF-κB and subsequently alter the ductular reaction/inflammation/fibrosis signaling pathways. (B) The expression levels of key mediators of NF-κB signaling pathway are altered in Pre-let-7a-transfected H69 human cholangiocytes after LPS stimulation relative to Pre-miRNA-Con. Relative gene-expression profile between Pre-let-7a-transfected H69 cells after LPS stimulation versus Pre-miRNA-Con is shown. The expression of a panel of diverse inflammation-associated genes was evaluated by real-time PCR assay using the Human Chemokines & Receptors PCR Array (PAHS-022; SABiosciences Corp., Valencia, CA), which was selected based on IPA with a focus on the NF-κB signaling–associated gene list. Gene expression relative to GAPDH was plotted as the volcano plots, depicting the relative expression levels (Log10) for selected genes in Pre-miR-Con versus Pre-let-7a (left panel). The relative expression levels and P values for each gene in the related samples were also plotted against each other in the scatterplot (right panel). The key mediators of NF-κB signaling pathway, NF-κB1, IkBα and IL-13, are the most altered genes in Pre-let-7a-treated H69 cells after LPS stimulation. Data represent the mean from three separate experiments. (C) Total RNA was isolated from CK-19-positive cells collected from ductular reaction fields in control and LSCEV-treated MDR2−/− mice liver sections by LCM, and Taqman real-time PCR assay and real-time quantitative PCR assay were carried out to detect let-7a and let-7c expressions, along with the mRNA expressions of inflammation/fibrosis markers (IL-13, NF-κB1, and NR1H4). LSCEV treatment significantly increased the biliary expression of let-7 in ductular reaction fields in MDR2−/− mice, along with the significant reductions of inflammation/fibrosis markers IL-13, NF-κB1, and NR1H4 when compared with the relative controls. *P < 0.05 relative to WT controls; #P < 0.05 relative to MDR2−/− controls. (D) Total RNA was collected from cholangiocytes isolated from the ductular reaction areas of liver sections from PSC patients by laser capture microdissection compared with healthy controls, and real-time quantitative PCR analysis was performed as described in the Materials and Methods. The miRNA and mRNA expression of let-7 (let-7a and let-7c) and inflammation/fibrosis markers (IL-13, NF-κB1, and NR1H4) were increased, whereas IκBα was decreased, in the cholangiocytes from ductular reaction fields from PSC patients’ liver compared with healthy controls. *P < 0.05 relative to normal controls. (E) Phosphorylation of IkBα (top panel) and degradation of IkBα (bottom panel) were detected in ductular reaction fields by double-staining immunohistochemistry analysis using cholangiocytes specific marker CK-19 plus phosphorylation or total IkBα antibodies in LSCEV-treated MDR2−/− mice liver relative to controls. (F) IL-13 expression and NF-κB nuclear translocation detected ductular reaction fields (marker: CK-19) in LSCEV-treated MDR2−/− mice liver when compared with MDR2−/− and WT controls by double-staining immunohistochemistry analysis. Multiple antigen labeling was performed in the same tissue section using the VECTASTAIN systems. Specific enzyme substrates were incubated in sections to develop contrasting optimal color (IL-13/NF-κB, brown; CK-19, red). The representative images from four separate experiments are displayed. Original magnifications: ×100 and ×50. Abbreviation: GAPDH, glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase.