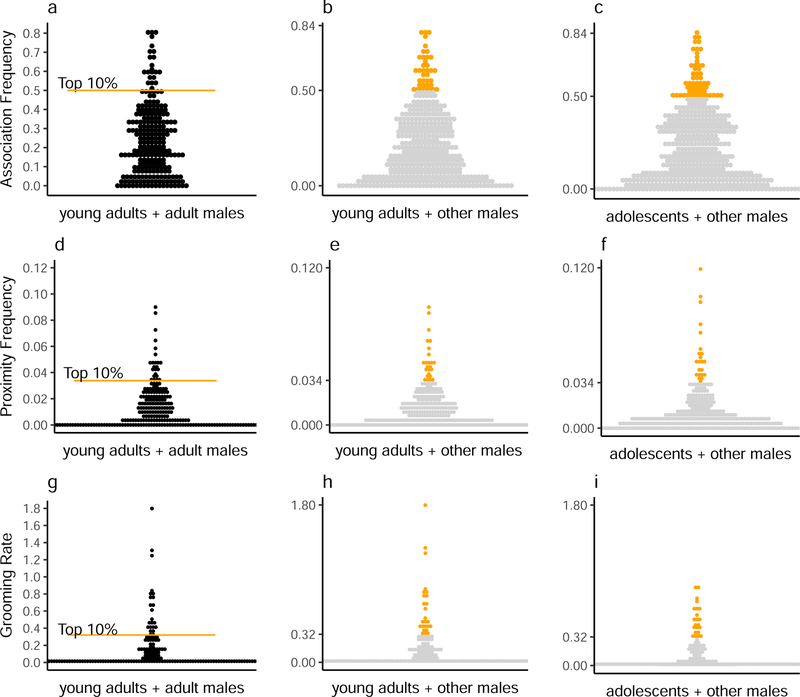
Figure 1.
Social bonds of adolescent and young adult male chimpanzees, identified as the top 10% of pairs in a sample of young adult males with other adult males separately for (a) association, (d) proximity, and (g) grooming. The value derived from the 10% threshold was used to classify bonds for young adults (b, e, h) and adolescents (c, f, i). Dyadic association frequencies represent the focal follows in association divided by total focal follows for the subject, proximity frequencies as the scans in proximity divided by total instantaneous point samples for the subject, and grooming rates as the total minutes grooming divided by hours of observation for the subject. Orange points are bonded pairs whereas gray points are those that fell in the lower 90% of the distribution based on the young adult-adult male distributions (a, d, g).